Service Provider Settings
Settings > Service Provider Settings
The Service Provider Settings provide options for ISVs to customize the user interface, brand the platform, and customize the user experience with personalized logos, art, fonts, color schemes, email messaging, campaigns, and more.
- Compare to: MSP Settings, a set of configuration options for MSPs
1 Working with Service Provider Settings
Users that have the Manage Tenants and Company Capabilities permission can manage Service Provider Settings
1.1 Prerequisites
When configuring Service Provider Settings, have the following information should be available:
- Name of your Service (Domain Name), Email Support Address (Secure Email Service Provider Name), Terms of Service
- Header and Footer HTML code (Brand messaging that appears at the top and bottom of some pages: Login, Logout, Password Reset)
- Header and Footer image/logo (Images that appear in the Header/Footer areas)
- Default applications to be loaded during user registration
- Starting application for a newly registered user
- Application Catalog URL
- Page that lists available applications; Users will install applications from this page
- Default is https://na.longjump.com/networking/Service?t=9
- Customization settings for the Customer Welcome Email (Personalize the message with the user's name, login name and password)
1.2 To Change Settings
- Click Settings > Service Provider Settings
- Select one of the configuration options below.
- Make changes:
- a. If it exists, click the [Edit] button, make changes, and then click [Save].
- b. Otherwise, click one of the links in the page to work with that option.
- Configuration options:
- Service Configuration - Customize service configuration settings
- Service Header HTML - Customize service header
- Service Footer HTML - Customize service footer
- Service Header Image - Customize service header logo
- Manage Email Templates - Customize email templates
- Manage Catalog - Customize the Catalog packages (requires the same kind of format as the default catalog page noted above)
2 Service Configuration
Settings > Service Provider Settings > Service Configuration
2.1 Basic Service Configuration
These values define the basic service configuration:
2.1.1 First-Time Service Configuration
- Configure the Service Settings and specify Service and Domain names:
Parameter Description Typical Value Service Name Name of the service provider Financiocorp Services Prefix for Service Domain Optional, a subdomain name - Learn more: About the Prefix for Service Domain
Allowed characters: a-z, A-Z, 0-9, - (alphanumeric, plus hyphen)
Example: service
Service Domain Name of the service domain, part of the URL - See Domain Name for more information
mydomain.com Domain URL Read Only
Automatically populated, created from Prefix + Primary Service Domain
service.mydomain.com service.otherdomain.com
2.1.2 Subsequent Configuration
These additional parameters become available after the initial configuration is complete.
Parameter Description Typical Value Recaptcha Private Key After signing up for Google's Captcha implementation of the Captcha service, enter the public and private keys here. (They are used to interact with that service.) Recaptcha Public Key Error Notification Email Address An email message is sent to this address when errors occur customer_support@mydomain.com No Reply Email Address The email address to use for messages sent by the platform, when replies are not permitted systemadministrator@mydomain.com Help Domain Required field; Domain name for user help; This page is opened in a new browser window when Help is invoked from the platform http://www.mydomain.com/help Custom Help Domain Optional; If present, it is the domain name for user help; Can be used with a custom Help URL in Custom Object
http://www.customhelp_mydomain.com Or, with Help URL http://www.customhelp_mydomain.com/userdefined_object_name
Document Directory File location for Documents /usr/local/ Temp Directory Used as a temporary storage location /temp/
2.1.3 Service Domain
- The Primary Service Domain and Alternate Service Domain names are configured in Service Provider Settings and comply with the following guidelines:
- Service Domain names can contain the following characters:
- alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9)
- hyphen (-)
- period, dot, full stop (.), used as the delimiter in the Prefix for Service Domain
- Considerations for the Service Domain
-
- The Service Domain is required
|-valign="top" |serviceproviderdomain.com | MSPdomain.com |www.abcde.serviceproviderdomain.com
www.abcde.MSPdomain.com |}
2.1.4 Prefix for Service Domain
This defines the subdomain name for the service. The subdomain name can only accept alphanumeric characters or the underscore character.
- Examples
Prefix for Service Domain Service Domain Domain URL(Read Only) www.abc.com www.abc.com xyz www.abc.com xyz.abc.com xyz abc.com xyz.abc.com
2.1.5 Help URL and Custom Help Domain
As a Service Provider, you might create a help website to align with a customer's branded instance of the platform. In this case, the URL of this help website would be used as the default Help Domain. When a user clicks the Help link in the platform, this default Help Domain opens in a new browser window.
The Custom Help Domain operates like the Help Domain, however it has an added benefit: it can be combined with the Help URL function to create custom help links for Custom Objects (excludes Built-in or CRM objects).
The following sections describe typical situations and the result when a user clicks the Help ![]() icon in a Custom Object.
icon in a Custom Object.
2.1.5.1 How the Custom Help Domain and Help URL Work
- The platform automatically checks for http/https protocols; If they are not present, they are prefixed to the Help URL
- The custom Help URL can be an Absolute URL or it can be combined with the Custom Help Domain as a Relative URL:
- Absolute URL Example
Custom Help Domain not applicable (When the Help URL is specified as an absolute URL, this value is ignored)
Help URL for an Inventory object http://www.mydomain.com/help/inventory Result: Click the Help icon in the Inventory object to invoke help at: - http://www.mydomain.com/help/inventory
- Relative URL Example
Custom Help Domain www.customhelp_mydomain.com Help URL for an Inventory object inventory Result: Click the Help icon in the Inventory object to invoke help at: - http://www.customhelp_mydomain.com/inventory
2.1.5.2 The Effect of Custom Help Domain and Help URL Settings
Both the Custom Help Domain and the Help URL are optional. These examples describe how user help is provided when these values are specified or omitted.
- Custom Help Domain and Help URL are specified
- All the specified Help URLs for Custom Objects are treated as relative to Custom Help Domain if they do not start with http:// or https://
- Example:
Custom Help Domain www.customhelp_mydomain.com Help URL inventory Resulting help URL for the object is: http://www.customhelp_mydomain.com/inventory
- Example:
Custom Help Domain www.customhelp_mydomain.com Help URL http://myhelpdomain.com/inventory Because the http:// is specified in the Help URL, the Custom Help Domain information is not used
Resulting help URL for the object is: http://myhelpdomain.com/inventory
- Custom Help Domain is not specified
- The Custom Help URLs for objects are treated as complete URLs and are used to display help
- Example:
Custom Help Domain: n/a Help URL http://myhelpdomain.com/inventory Resulting help URL for the object is: http://myhelpdomain.com/inventory
- Custom Help Domain and Help URL are not specified
- A generic help URL is formed using the 'Help Domain' field in Service Provider Settings.
- Example:
Custom Help Domain: n/a Help URL: n/a Resulting help URL for the object: Reverts to the default Help Domain
2.2 Support Service Configuration
This information is published for users to contact you regarding your service.
- When tenants publish Packages, this email address receives the notification
Parameter Description Typical Value Support Organization Name of the Support Organization Service Provider Support Team Support Email Email address to send support requests support@mydomain.com Available Case Types Picklist of types of support cases
2.3 Email Configuration
Configuration for all the emails sent from the LongJump Platform.
Parameter Description Typical Value Hostname For Relay Server Hostname localhost User Name User/login name for the email relay server Password Password related to the user/login name for the email relay server
2.3.1 Bounced Email Configuration
This email configuration will process all the bounced emails sent through the platform. When an email message does not reach the recipient, it is returned (considered "bounced"). This can happen when an email address is no longer active, or because the recipients' email box is full.
To enable Bounced Email Processing:
- From the Email Configuration section, complete the following information:
- Enable Bounced Email Processing
- Click the checkbox
 icon to enable processing for bounced email messages and complete the information in the required fields
icon to enable processing for bounced email messages and complete the information in the required fields
- Click the checkbox
- Optionally, Enable Bounced Email Processing to the Alternate Service Domain
- Click the checkbox
 icon to enable processing for bounced email messages and complete the information in the required fields
icon to enable processing for bounced email messages and complete the information in the required fields
- Click the checkbox
Parameter Description Typical Value Enable Bounced Email processing Email Bounce Address Checkbox: Yes/No Hostname Hostname pop.my_secure_email_provider.net Mailbox Address Email Mailbox Address bounce@myemailprovider.com Mailbox Password Specify the password for this email account T0pS3cr3tPa$$word
2.4 External Email Tracking Configuration
To enable external email tracking, set the following attributes to initialize the service:
Parameter Description Typical Value Enable External Email Tracking Option to enable External Email Tracking Checkbox: Yes/No Hostname Specify the email provider hostname that manages email messaging to/from your site pop.my_secure_email_provider.net Mailbox Address Specify the email address used for email messaging to your site service@mydomain.com Mailbox Password Specify the password for this email account T0pS3cr3tPa$$word
Important:
Set up a "catch-all" mailbox in a separate domain to accept messages of the form xyz@your-special-domain.com.- Messages are deleted from the mailbox after they are read, so you don't want to use your standard mailboxes.
- A catch-all mailbox collects everything sent to the specified domain.
(That way, you don't have to set up a separate mailbox for each user.) - Using a separate domain ensures that none of your regular mail goes into the catch-all mailbox.
Learn more: Catch-all mailboxes
2.5 Process Workflow by Email Configuration
Workflows can be email-enabled, using these attributes:
Parameter Description Typical Value Enable Workflow By Email Option to allow Workflow managment via email Checkbox: Yes/No Hostname Specify the email provider hostname that manages email messaging to/from your site pop.my_secure_email_provider.net Mailbox Address Specify the email address used for email messaging to your site service@mydomain.com Mailbox Password Specify the password for this email account T0pS3cr3tPa$$word
Important:
Set up a "catch-all" mailbox in a separate domain to accept messages of the form xyz@your-special-domain.com.- Messages are deleted from the mailbox after they are read, so you don't want to use your standard mailboxes.
- A catch-all mailbox collects everything sent to the specified domain.
(That way, you don't have to set up a separate mailbox for each user.) - Using a separate domain ensures that none of your regular mail goes into the catch-all mailbox.
Learn more: Catch-all mailboxes
2.6 Service Theme and Stylesheet
Parameter Description Theme Select a default Theme; Defines the color for the tabs, background and highlight colors Allow Users to Change Theme Optionally, allow users to personalize the color scheme for their pages. Checkbox: Yes/No URL for Custom Style sheet Specify the URL for a CSS (Cascading Style Sheet) that is applied to all pages UI Container Scripts CSS style sheet declarations, javascript declarations, or any other HTML elements to be included in the header of each page.
2.7 Develop Configuration
Java code running in a tenancy is subject to strict limits--or governors:
- Some settings put limits on the number of resources that tenants can use, to prevent infinite loops and other kinds of runaway programs. The limits apply to each tenant execution interval--from the time that the platform application instance gives control to tenant code, until the time that control returns to the platform. Up to that limit, an application can use as many resources as it wants. But once a constraint is exceeded, the executing code aborts with an exception.
- Other settings restrict the kinds of Java classes that can be used, to prevent unwarranted access to the server and/or security violations.
The Service Provider Settings can be used to tighten those restrictions, ameliorate them, or lift them entirely.
- Considerations
-
- Settings are global. They apply to all tenants in the platform instance.
- Settings apply to scheduled (background) jobs, as well as foreground applications.
- The minimum for all numeric settings is "1".
- Changes to these settings take effect only when the platform application instance is restarted.
Here are the default settings:
Parameter Description Default Value Apply Governors in Java Code? Whether or not governors are applied to this platform instance. A development instance may want to turn them off, in some cases. Any multi-tenant production instance will want them on, to ensure that a runaway program in one tenant does not interfere with other tenants. Yes Max Number of Statements allowed The maximum number of Java code statements that can be run during an execution interval. 10000
Maximum String Length allowed The total size of all strings allocated in the Java heap space during an execution interval. 30000
Maximum CPU Time allowed (milliseconds) The maximum number of CPU milliseconds that can be consumed during an execution interval. 60000
Java classes not allowed in code There are certain Java classes which are disallowed in tenant classes, to prevent access to the server and any compromise of server security. (They are, however, allowed in global classes developed by the ISV for use by all tenants.) In order to protect the security of the server, enter a comma-separated list of fully qualified Java Class Names for this option. At compile time, application will check if any of these classes are referenced in the user code and throw an exception if they are. Note that this will take effect only after the server is restarted.
java.lang.System, java.lang.Runtime, java.lang.Class, java.lang.ClassLoader, java.lang.Thread, java.lang.ThreadGroup, java.lang.ThreadLocal, java.lang.Runnable, java.lang.Compiler, java.lang.RuntimePermission, java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject, java.lang.reflect.Array, java.lang.reflect.Constructor, java.lang.reflect.Field, java.lang.reflect.Method, java.lang.reflect.Modifier, java.lang.reflect.Proxy, java.lang.reflect.ReflectPermission, java.io.FileReader, java.io.FileWriter, java.io.FileInputStream, java.io.FileOutputStream, java.net.DatagramSocket, java.net.DatagramSocketImpl, java.net.HttpURLConnection, java.net.Inet4Address, java.net.Inet6Address, java.net.InetAddress, java.net.InetSocketAddress, java.net.JarURLConnection, java.net.MulticastSocket, java.net.ServerSocket, java.net.Socket, java.net.URL, java.net.URI, java.net.URLClassLoader, java.net.URLConnection, java.net.URLStreamHandler
Libraries supported in Java Code When compiling user-defined code, the platform allows certain libraries like jars or internal java packages:
- If a custom library is required, the jar can be placed in the ../tomcat/lib folder of the Apache Tomcat installation
- To include these library files, enter a comma-separated list of such jar files for this option
- Note that this will take effect only after the server is restarted.
Empty
No. of Objects in Database Views Database Views allow the creation of custom categories that join multiple objects
- These database views can be used as the base category for a View or a Report
- The maximum number of tables that are allowed is five (5), with a default value of three (3)
- The number of joins in these tables is restricted to the maximum number + 1
Default: 3, Range is 3-5 Maximum rows in a view Maximum number of rows that are fetched in a List Display for an object is defined by this option
- This number is limited by the maximum int value supported by Java/MySQL i.e. 2^16 = 4G
10000 Maximum rows in a report - Maximum number of rows that are fetched in a report
- This number is limited by the maximum int value supported by Java/MySQL i.e. 2^16 = 4G
5000 Maximum rows in a Scheduled Report - Maximum number of rows that are fetched in a report that runs in the background queue.
- This number is limited by the maximum int value supported by Java/MySQL i.e. 2^16 = 4G
5000 Maximum Savepoints Intermediate placemarks, which identify points at which the data fields contain intact, legitimate values 5 Maximum Recursions in Java API Allow a function to call itself the specified number of times 10
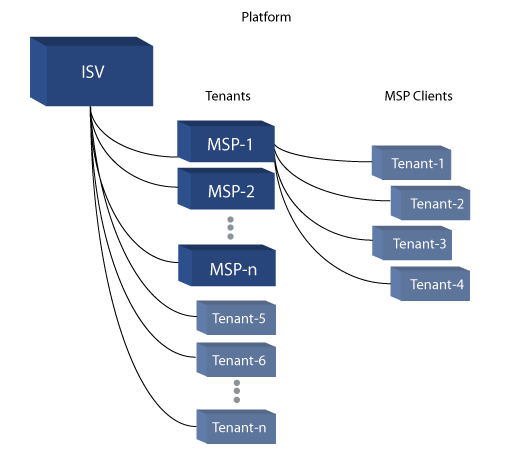
2.8 Tenant Configuration
- This section is used by:
- ISVs and MSPs who are hosting clients on a shared instance of the platform.
- ISV users who are setting up an instance of the Installable Version in order to Develop on Separate Platforms.
- Allow Unauthenticated Tenant Creation
- Allows any prospective customer to create a new tenancy (a trial account).
- Unchecked by default
- If checked, trial accounts can be created by unauthenticated users who have a computer and network connection that meets the Minimum System Requirements
- Enable Tenant Subdomains
- This setting lets customers specify a URL subdomain when registering, giving them a unique URL they can use to access their platform applications.
- Learn more: Tenant Subdomains
2.9 Catalog Configuration
Configuration for application Packages:
- Considerations
-
- This is the older format used to display a list of published packages. In this format, only an image and a short description are displayed for each package. The newer Community Marketplace functionality can be selected in the Community section that follows. That format allows more Catalog Information to be displayed for each application package.
- If you want to use this functionality, you should disable the Community Tenant defined in the next section. Otherwise, you should clear the Package Catalog URL field.
- The list of Packages available for installation can vary, depending on whether packages are approved for publication, and whether the approval comes from the ISV or the MSP.
- Packages approved by an MSP are available to MSP users and MSP tenants.
- Packages approved by the ISV are available to ISV users.
- By default, such packages are available to MSP users and their tenants, as long as the MSP has Include Global ISV Catalog option enabled in their MSP Settings.
- Learn more: Manage Catalog
2.10 Community Site Configuration
The community site is not enabled, by default. When enabled, all users in all tenancies supported by an ISV can access and use the Community features.
- Community Site settings
-
- Enable Community
- Checkbox. Disabled by default. Click it to enable the community feature.
- Community Tenancy ID
- Read-only display of the Community Tenant ID.
- Community Site Name
- Read-only display of the name displayed on each community page.
- Marketplace Service Domain
- The Community Marketplace is a newer format for a list of approved packages that are available for installation. It provides a richer interface than the older Catalog format, and allows much more Catalog Information to be displayed for application packages.
- Providing a value in this field activates the Community Marketplace.
- The value can be the service's domain name with an optional subdomain, or the service's IP address.
- Considerations
-
- The specified domain or IP address must match the Service Domain specified for this installation.
- If Tenant Subdomains are enabled, a subdomain can be specified using the format {subdomain}.{domain}.
For example: applicationcatalog.yourService.com. - If this value is specified, the Package Catalog URL field in the section above should be cleared.
2.11 Global Tenancy
From the designated tenancy, specified objects and the data they contain can be shared with other tenants who have installed a package that contains those objects.
Learn more: Global Data
- Global Tenancy ID
- The ID of tenant from which objects are shared.
- Global Tenancy Shared Object List
- A comma separated list of Object IDs that are shared.
2.12 Registration Configuration
Choose the default settings for new tenants:
- Registration Sidebar
- HTML for the Sidebar on the user registration page. (If empty, this section of the registration page is not displayed.)
- App Center Sidebar
- Specify HTML to display in the Sidebar of the App Center. For example, use it to display images that link to a package catalog, videos, training, and other resources.
- Enable App Center
- Gives tenants access to the My Applications / App Center functionality.
- If enabled:
- A [My Applications] button appears in the GUI.
- Clicking it takes the user to the App Center.
- Installed applications are listed in the My Applications tab
- The specified HTML is displayed in the Sidebar.
- The user has access to wizards to create objects, import spreadsheets, and establish Object Relationships.
- Many-to-Many relationships can be created merely by specifying the desired relationship.
(The inner Junction Objects are created automatically.)
- If disabled:
- An [Applications] button appears in the GUI.
- Clicking it displays a dropdown list of applications.
- A link in that list takes the user to the application Catalog.
- Wizards are not available.
- Many-to-Many relationships are established manually, by creating the junction object and creating the appropriate Lookup relationships to the endpoint objects.
- If disabled:
- URL for Terms of Service
- URL of the Terms of Service page, created by the ISV
- Optionally, MSPs can supply a URL to a custom Terms-of-Service page. (If empty, this section of the registration page is not displayed.)
- Enable Relay for new Tenants
- Enable the social-networking application, Relay, so users in a tenancy can form groups, follow posts, and track changes to data. (Each tenant can then turn it on or off in their Company Information settings.)
2.13 Starting Application Configuration
- From this section, choose the starting application for newly registered users.
Users can change the default starting application at a later time
- From this section, choose the starting application for newly registered users.
3 Service Header HTML
Settings > Service Provider Settings > Service Header HTML
The Service Header appears at the top of the page (header), and defines the stylesheet for these pages:
- Login
- Logout
- Applications Catalog
- Reset Password
Find a cut-and-paste example: Service Header HTML Code Sample
To Edit the Service Header HTML:
- Enter Raw HTML Text (Copy & Paste Raw HTML) into the editing area
- Click [Save]
Settings > Service Provider Settings > Service Footer HTML
The Service Footer appears at the bottom of the page (footer), and defines the stylesheet for these pages:
- Login
- Logout
- Catalog
- Reset Password
Find a cut-and-paste example: Service Footer HTML Code Sample
To Edit the Service Footer HTML:
- Enter Raw HTML Text (Copy & Paste Raw HTML) into the editing area
- Click [Save]
5 Service Header Image
Settings > Service Provider Settings > Service Header Image
Use this option to change the Service Header logo. This logo appears in the heading area of every page. Required dimensions: 900px by 55px.
6 Manage Email Templates
Settings > Service Provider Settings > Manage Email Templates
With these options, Service Providers can personalize communications with tenants and build value with customized branding and messaging.
Template variables can be used to personalize the Subject or Body of the message.
- Learn more:
6.1 Managing Email Templates
To edit an email template:
- Click Manage Email Templates
- Select a template from the list
- Click [Edit], and modify the settings:
- Email Subject
- Subject of the email message
- Use Email Header & Footer
- Default is Yes; if enabled, displays the Service Header HTML and Service Footer HTML
- HTML Email Body
- HTML code is provided, which can be edited in place, or replaced (via cut-and-paste action from an HTML editor).
Manage Email Header/Footer Settings
- Email Header HTML
- Email Footer HTML
Use this option to specify the Email Header and Footer HTML code used in system-generated Email Notifications. Examples of typical system-generated email notifications are:
- Task status update/notifications
- Welcome email message sent to new users
- Appointment reminder email messages
The HTML code creates a template for system-generated messages, and can be used to brand your notification messages.
- Email Header HTML - appears at the top of system-generated email messages
- Email Footer HTML - appears at the bottom of system-generated email messages
Find cut-and-paste examples here:
6.1.2 Tenant
Manage Tenant Welcome Messages:
- Tenant Self-Registration Welcome Email
- Tenant Registration by ISV/MSP Welcome Email
- Email Verification
6.1.3 User
Manage User Notification Related Emails:
- User Welcome Email
- Used in messages sent when a user account is created, and provides a link to the Login page
- Reset Password Email
- Used in messages sent when the user password has been reset, and provides the user's password
- Forgot Password Link Email
-
- Used in messages sent when the user clicks the Forgot my Password link, and provides a link to the Security Question
- Learn more: Login
- Forgot Reset Password Email
-
- Used in messages sent after a user requests a password change, and provides a new, temporary password
- Also used when a new user/tenant is added via REST API - Add a User, and a password not specified when the user record is created
6.1.4 Task
Manage Task Notification Related Emails:
- New/Edit Task Email
- Change new/edit task email template
- Task Completed Mail
- Change task completed email template
- Task Reminder Email
- Change task reminder email template
- Project Task Reminder Email
- Change project task reminder email template
- Send Note Email
- Change send note email template
6.1.5 Appointment
Manage Appointment Notification Related Emails:
- New/Edit Appointment Email
- Appointment Reminder Email
6.1.6 Status
Templates for Status Notification Emails:
- Export Status Email
- Mass Operation Status Email
- Import Status Email
- Report Status Email
- Translation Export Status Email
6.1.7 Package
Templates for Package Notification Emails:
- Package Approval Email
- Package Rejection Email
- Package Publish Email
- Package Deploy Notification Email
6.1.8 Storage Notifications
Set Up Templates for Storage Notifications:
- 90% Storage Space Exhausted Status Email
- 100% Storage Space Exhausted Status Email
6.1.9 Case
Manage Case Related Notification Emails:
- New Suppport Case Notification Email
- Support Case Update Notification Email from Provider
- Support Case Update Notification Email from Customer
6.1.10 Other
Manage Other Notification Emails:
- Ownership Change Mail
- Accessories exceeded notification email
- Templates to used when:
- Scheduled Job Limits exceeded
- API Calls Limit exceeded
7 Manage Catalog
Settings > Service Provider Settings > Manage Catalog
Configure Catalog options.
- Catalog
- View the current Catalog
- Approve Packages
- Review Packages pending approval
- User can either:
- [Approve] package for publication to the catalog
- [Reject] package, and deny publication to the catalog
- In either case, an email is sent to the submitter, to tell them the outcome.
- Learn more: Package Approval or Rejection
- Select Packages
- Choose the packages to display in the Catalog
- User can either:
- Move a package into the Visible column to display the package in the catalog
- Move a package into the Hidden column to remove the package from the catalog
- Set the order of the list of Packages in the catalog
- Considerations
-
- If an ISV moves a package from the Visible column to the Hidden column, it is removed from all the Tenant and MSP Catalog pages, and is no longer available for installation.
- If an ISV moves a package from the Hidden column to the Visible column in Manage Catalog, the package will be displayed in the Tenant and MSP Catalog pages.
- If an MSP removes a package from the MSP Catalog, it is removed from that MSP Catalog page only, and is no longer available to the Tenants of that MSP.