Difference between revisions of "SAML"
imported>Aeric |
imported>Aeric |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
===SAML Settings=== | ===SAML Settings=== | ||
<blockquote> | <blockquote> | ||
;SAML Version: ''Version 2.0'' | ;SAML Version: ''Version 2.0'' | ||
Revision as of 11:34, 12 April 2016
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-based standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between security domains. The Service Provider must enroll with an Identity Provider and obtain an Issuer URL.
How it Works
An enterprise app contains a link to the AgileApps Cloud platform. When users who are logged into the enterprise app click that link, they are automatically logged into the AgileApps Cloud platform, without requiring additional authentication. For example, an employee of ABC Company logs into the corporate website, which includes a link to the AgileApps Cloud platform on the landing page. The user clicks the link and is automatically logged in, without requiring a second login.
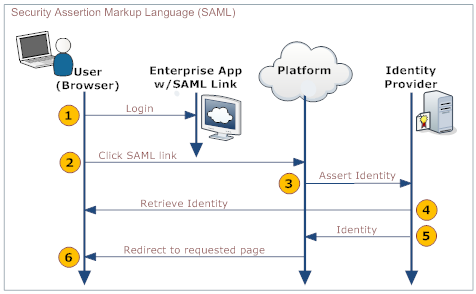
The process is shown in the following diagram:
Here is an explanation of the steps:
User Your Organization's Web App Platform Identity Provider 1. Logs in to a web app provided by your organization - Provides a link to the platform's SAML handler (generated by the platform when SAML is configured)
- Includes the desired platform target page as an argument in the link
2. Clicks the link that goes to the SAML handler 3. Sends an assertion to the identity provider 4. Retrieves and validates the user's identity 5. Sends the user's identity to the platform 6. Redirects the user to the appropriate page.
Enabling SAML
- Click
 > Administration > Account Management > Single Sign-On
> Administration > Account Management > Single Sign-On - Click the [Edit] button
- For Single Sign-On Settings, choose SAML
- Fill in the SAML Settings (below)
- Click [Save]
The platform generates a link that goes to the SAML platform's SAML handler.
SAML Settings
- SAML Version
- Version 2.0
- Issuer
- The identity provider. (A name or identifier of some sort.)
- SAML Third Party authentication URL
- The URL used to authenticate a user or maintain a user's credentials.
- Syntax:The URL and Port Number must be specified using a FQDN or an IP address, for example:
- www.abc.com:9090
- 192.168.1.10
- abc.def.com
- SAML Request Issuer URL
- The URL used to access this tenant. Ex: http://yourCompany.agileappscloud.com
- User Id Type
- Determines the type of identifier
- Choose UserId or Federated Id, where:
- UserId is the Record Id of the user that is logged in
- Federated ID acts as a user's authentication across multiple IT systems or organizations.
- Learn more: Federated Identity
- User Id Location
- Specifies an attribute tag that defines the location of the User Id
- Choose Subject or Attribute
- Attribute for User ID
- Specify the Azure attribute that contains a platform User ID.
- If the User ID attribute is empty, or does not match an existing user then either login fails or a new user is created, depending on the next setting.
- Create New Users
- Check this box to create a new user when the User ID is not recognized.
- When checked, additional options appear to specify default values and attribute-fields to use for the User's team, access profile, application, and role:
- Default Team - A new user's default Team.
- The team assignment can be changed in the platform after the user logs in.
- The user can change it in their Personal Settings. An admin can do so in the Users page.
- Default Access Profile - A new user's default Access Profile.
- The user's access profile is fully determined by the configuration.
- LDAP Attribute for Access Profile - The name of the LDAP attribute that designates the user's access profile.
- The attribute must contain an access profile's record ID.
- To get a record ID:
- a. Go to
> Access Management > Access Profiles
- b. Modify the view to display Record IDs, and copy the ones you need.
- Default Application - The initial Application the user sees when they log in.
- That setting can be changed in the platform after the user logs in.
- The user can change it in their Personal Settings. An admin can do so in the Users page.
- To grant access to additional applications:
- a. When the user logs in, a User record is created for them in the platform.
- b. You can then use the Application Access page to specify the applications the user can access.
- LDAP Attribute for Application - The name of the LDAP attribute that designates the user's application.
- The attribute must contain the application's record ID.
- To get a record ID:
- a. Go to
> Access Management > Application Access
- b. Modify the view to display Record IDs, and copy the ones you need.
- Default Role - The new user's Role in the application.
- That setting can be changed in the platform after the user logs in.
- The user can change it in their Personal Settings. An admin can do so in the Users page.
- LDAP Attribute for Role - The name of the LDAP attribute that designates the user's role in the application.
- The attribute must contain the role's record ID.
- To get a record ID:
- a. Open the application, if it is not already running.
- b. Go to
> Customization > Application Roles
- c. Modify the view to display Record IDs, and copy the ones you need.
- Issuer Certificate
- Issuer certificate is used to sign and verify SAML messages. Requires a valid x509 issuer certificate.
- Choose one of the following options:
- Paste the Issuer Certificate in the text area
- Navigate to the Issuer Certificate section, then select and load a file containing the Issuer Certificate
Using SAML
To use single sign-on with SAML, you create links that go to the platform's SAML handler, passing the desired destination page as an argument.
To create a link to the platform in your enterprise app:
- Copy the SAML link that was generated when SAML was configured.
- Add a done= argument to the link that specifies the target page in the platform.
To create the done= argument:
- Go to the standard initial page using Service?t=1&targetpage=ViewPort.jsp
- Visit the page you want to target
- Copy the URL from the browser's address bar
- Edit the URL to remove https://{yourDomain}/networking/"
What remains is the argument you'll pass. For example: pages/yourPage.jsp - URL encode the link
- Learn more: URL Encoding