Difference between revisions of "Application Architecture"
From AgileApps Support Wiki
imported>Aeric |
imported>Aeric |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
An application running on the {{enterprisebrand}} can be as simple as single JSP page, or it can combine multiple resources, as shown in the following diagram. (The numbers indicate the lab exercise that introduces that facet of the platform.) | An application running on the {{enterprisebrand}} can be as simple as single JSP page, or it can combine multiple resources, as shown in the following diagram. (The numbers indicate the lab exercise that introduces that facet of the platform.) | ||
:<table> | |||
<tr><td>[[File:dev_app_architecture.png]]</td> | |||
<td> | |||
[[File:ISV_add_JARs.png]] | |||
<br> ([[On-Premise Installation]] option) | |||
</td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
Here's how those components work together: | |||
;JSP Page: A JSP [[Page]] provides the user's '''view''' of the application. That view can be further enhanced using the library of {{^jQuery}} components that is at your disposal, and you can use either the [[Java API]] or use [[AJAX and REST]]. | |||
[[ | ;Java Controller class: In the best tradition of the [[Working with Pages and Classes#MVC|MVC]] architecture, a Java class acts as the '''controller'''. It implements the [[Controller Interface]], responds to user requests, and interacts with the data store. That class makes it easy to take the user's browser to the next step in the processing flow. It can be further augmented with additional classes, and with [[Static Resources]] files. Output statements can be sent to a [[Debug Log]] to help diagnose problems. | ||
;Controls Library: Access and manipulate the Document Object Model (DOM) using {{^jQuery}} functions. Add jQuery controls to the page. Invoke JSON functions. Make JavaScript calls to retrieve XML or Json data. | |||
; | |||
; | ;Static Resources:To assist in the presentation of JSP pages, CSS files and JavaScript files can be stored and accessed from the page. | ||
;Data Store:The data store constitutes the application's data '''model'''. Under the covers, it's a relational database with all the [[Data Management]] trimmings (MySQL). But to an application developer, the data looks like Java objects, rather than rows in a table--so applications are easier to develop, and the whole task of database administration is offloaded to the platform. | ;Data Store:The data store constitutes the application's data '''model'''. Under the covers, it's a relational database with all the [[Data Management]] trimmings (MySQL). But to an application developer, the data looks like Java objects, rather than rows in a table--so applications are easier to develop, and the whole task of database administration is offloaded to the platform. | ||
;Java Class Libraries: | ;Java Class Libraries:Access the standard libraries that provide the platform's [[Java API]]. Incorporate Java code directly into your JSP pages, or create Java classes to maximize functionality and reuse. | ||
; | ;Back End Design Elements: | ||
:;Events and Business Rules: Use conditional [[Rules]] to invoke Java methods and launch processes. Optionally trigger additional Rules when you update data. | |||
:;Processes and SLAs:Use [[Processes]] to invoke business rules, create Tasks for users, and send messages. Define [[SLAs]] to make sure things happen in timely fashion. (SLAs are effectively time-dependent processes that create tasks, send emails, and carry out other actions.) | |||
:;Web Services: Configure [[Web Services]] to send data to remote services, and to retrieve data from them. | |||
;Debug Log:In addition to the event log, a special debug log can be used to track messages sent by application code. | ;Debug Log:In addition to the event log, a special debug log can be used to track messages sent by application code. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 35: | ||
;REST interfaces:All applications running on the {{enterprisebrand}} are built from the application components listed above. [[REST]] interfaces can be used to log on to the system, access the applications, and interact with them. | ;REST interfaces:All applications running on the {{enterprisebrand}} are built from the application components listed above. [[REST]] interfaces can be used to log on to the system, access the applications, and interact with them. | ||
[[Category: | ;Custom JARs: With the [[Installable Version]], ISVs can add additional Java ARchive files (JARs)--for example, to integrate with external systems, utilize custom Web services, or access an existing function library. | ||
<noinclude> | |||
[[Category:Application Design]] | |||
[[Category:Lab]] | [[Category:Lab]] | ||
</noinclude> | |||
Latest revision as of 23:21, 7 April 2014
An application running on the AgileApps Cloud platform can be as simple as single JSP page, or it can combine multiple resources, as shown in the following diagram. (The numbers indicate the lab exercise that introduces that facet of the platform.)
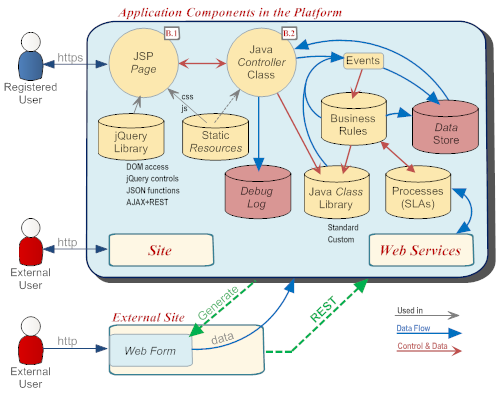
(On-Premise Installation option)Here's how those components work together:
- JSP Page
- A JSP Page provides the user's view of the application. That view can be further enhanced using the library of jQuery components that is at your disposal, and you can use either the Java API or use AJAX and REST.
- Java Controller class
- In the best tradition of the MVC architecture, a Java class acts as the controller. It implements the Controller Interface, responds to user requests, and interacts with the data store. That class makes it easy to take the user's browser to the next step in the processing flow. It can be further augmented with additional classes, and with Static Resources files. Output statements can be sent to a Debug Log to help diagnose problems.
- Controls Library
- Access and manipulate the Document Object Model (DOM) using jQuery functions. Add jQuery controls to the page. Invoke JSON functions. Make JavaScript calls to retrieve XML or Json data.
- Static Resources
- To assist in the presentation of JSP pages, CSS files and JavaScript files can be stored and accessed from the page.
- Data Store
- The data store constitutes the application's data model. Under the covers, it's a relational database with all the Data Management trimmings (MySQL). But to an application developer, the data looks like Java objects, rather than rows in a table--so applications are easier to develop, and the whole task of database administration is offloaded to the platform.
- Java Class Libraries
- Access the standard libraries that provide the platform's Java API. Incorporate Java code directly into your JSP pages, or create Java classes to maximize functionality and reuse.
- Back End Design Elements
-
- Events and Business Rules
- Use conditional Rules to invoke Java methods and launch processes. Optionally trigger additional Rules when you update data.
- Web Services
- Configure Web Services to send data to remote services, and to retrieve data from them.
- Debug Log
- In addition to the event log, a special debug log can be used to track messages sent by application code.
- Sites
- While registered users can log in and access applications over an https connection, it is frequently desirable to allow interactions from the general public--for example, to send suggestions or submit a resume. Sites let you carve out an area of the platform that can be accessed over a standard http connection, without requiring the user to log in.
- Web Forms
- While it's convenient to develop an application on the AgileApps Cloud platform, you may want to interact with users on a site that already exists. To do that, you generate Web Forms that use JavaScript to collect information from the user and send it to an application--for example, to get contact information from someone who wants to be in the loop on new announcements and product developments.
- REST interfaces
- All applications running on the AgileApps Cloud platform are built from the application components listed above. REST interfaces can be used to log on to the system, access the applications, and interact with them.
- Custom JARs
- With the Installable Version, ISVs can add additional Java ARchive files (JARs)--for example, to integrate with external systems, utilize custom Web services, or access an existing function library.