Single Sign-On
Settings > Administration > Single Sign-On Template:TenantFeatures
Single Sign-On provides the ability for users to gain access to multiple enterprise systems with a single login. A single login saves time for users, and simplifies their work, because they no longer have to stop to login again at every gateway to an application/portal/enterprise system.
Simplified SOAP Protocol for Single Sign-On
The platform's implementation of Single Sign-On uses simple SOAP messages sent over an HTTP connection. The resulting protocols are simple enough to be implemented in a minimum amount of time, making it easy for enterprises to integrate platform services into their existing operations.
- Best Practices
Consider the following best practices when implementing Single Sign-on for your organization:
- Your organization’s implementation of the Web service must be accessible by the platform servers. This means you must deploy the Web service on a server typically in your DMZ.
- Namespaces, element names, and capitalization must be exact in SOAP requests. Wherever possible, generate your server stub from the WSDL to ensure accuracy.
- For security reasons, you should make your Web service available by SSL only. You must use an SSL certificate from a trusted provider, such as Verisign or Thawte.
- The platform sends you the originatingIp in the web service call it makes to your servers. You can use this information to restrict access based on the user’s location.
- You must map your organization’s internal usernames and the platform's usernames. If your organization does not follow a standard mapping, you may be able to extend your user database schema (for example, Active Directory) to include the platform username as an attribute of a user account. Your authentication service can then use this attribute to map back to a user account.
- We recommend that you do not enable single sign-on for the system administrator’s profile. If your system administrators are single sign-on users and your single sign-on server has an outage, they have no way to log in to the platform. System administrators should always be able to log in to the platform so they can disable single sign-on in the event of a problem.
Enabling SSO in the Platform
Users with the System Administrator role can enable Single Sign On
Single Sign On must be enabled for each user, individually--typically when the user account is created in the platform.
- Learn more: Add a User
To configure Single Sign-On:
- Click Settings > Administration > Single Sign-On
- Click the [Edit] button
- In the Single Sign-On Settings section, choose one of the available options:
- Fill in the settings for the choice you made (described in the sections that follow)
Guidelines
- The System Administrator can decide to enable some users for SSO and disable SSO for other users. In this case, users with SSO enabled will be validated against their corporate environment and users with SSO disabled will be validated against the platform.
- SSO cannot be turned off if there exists at least one user who has SSO enabled from the user profile. If the System Administrator tries to disable SSO under this condition, a warning is displayed.
- If SSO is disabled, and the System Administrator tries to enable SSO for a user, the System Administrator is asked to enable SSO, and provide a valid SSO URL
- When disabling SSO for a User, the administrator is asked to use Reset Password for the user. This is to ensure that this user receives a valid password for login.
Restrictions
- Username in the platform should be same as the username in your organization's environment
- These password-related options are not allowed:
- Reset Password
- Change Password
- Forgot Password - a Message will be shown prompting the user to contact their organization's system administrator
- When adding a new user, the Welcome email message will not contain a password.
- SSO can be turned on/off at the user level, if the System Administrator has granted the user rights to change this setting
Delegated Authentication
With delegated authentication , you can use your own server to validate platform users against a corporate database or an LDAP Directory. You can use a single username and password to access all applications as long as the applications support delegated authentication.
Scope
Delegated authentication is limited to user authentication and does not include authorization. You must be active in the platform, and teams, roles, and other permissions must also be maintained.
The corporate System Administrator or the IT Staff develop and implement a web service that can accept and respond to the web service calls made by the platform servers.
Working with delegated authentication
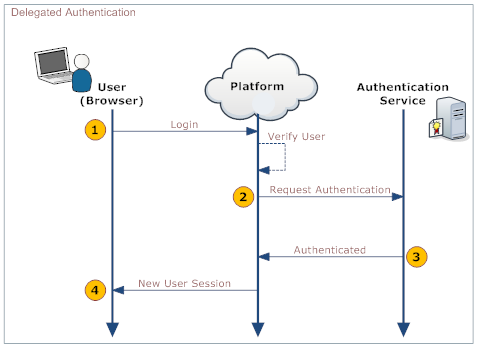
When you logon to the platform, your identity is authenticated in the platform and on your organization's systems. The following diagram shows the process:
This table describes the actions taken by the user, the platform, and your organization's Web Service.
User Platform Your organization's web service 1. Log on the platform Validate that: - User is active
- SSO is enabled
2. Make a web services call to the organization's web service, requesting authorization. Include the following parameters in the call:
- <syntaxhighlight lang="java" enclose="div">
username password originatingIp </syntaxhighlight> Note: originatingIp is the IP address that initiates the login request. This could be useful to restrict access based on the user's location. The web service must be implemented in a way that the platform is able to access it.
3. Validate the passed information and return either "Authenticated" or "Failure". 4. On Authenticated response, generate a new User Session. On Failure, notify the user.
Enabling delegated authentication
- Click
 > Administration > Account Management > Single Sign-On Settings.
> Administration > Account Management > Single Sign-On Settings. - Click the [Edit] button.
- Choose Delegated Authentication from the Single Sign-On Using drop-down list.
- Specify the URL of the authentication server running in your environment (abc5.abc.com:8080) in the SSO Gateway Url field.
- Note that the URL and Port number must be specified using a Fully Qualified Domain Name or an IP address. Secure HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer) protocol is used to access this URL. If you do not have this information available, contact your IT department or System Administrator.
- Choose whether or not to enable SSO for individual Users.
- Click [Save]
Setting up communication with the authentication server
The authentication server needs a certificate for a successful handshake with the platform. If you are using a self-signed certificate, it needs to be loaded into the cacert keystore file in the platform's {installed_JDK}/jre/lib/security folder. Unable to load the certificate displays an SSL error.
To load the certificate into the keystore:
- Check the configuration in the following three locations:
- installation.properties
- configure.pl installation script
- scripts/longjump
- Make sure that the JAVA_HOME environment variable points to the JRE in the installed JDK.
- For more information, see Platform Installation Files.
- Load the certificate using the keytool -import command.
- Note: The default password is changeit.
For more information , see Java Tutorial: Importing a Certificate.
Making a web service call
Use the URL and port number provided under the Single Sign-On Settings section to make a SOAP request to authenticate the users. SSO Request and SSO Response are predefined by the platform. These request and response are conducted via SOAP messaging.
Web services message format
- Request
- SSO SOAP Request sent from the platform is as follows:
- <syntaxhighlight lang="xml" enclose="div">
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soapenv:Body> <LJAuthenticate xmlns="urn:authentication.soap.ws.longjump.com"> <username>jim@abc.com</username> <password>sales</password> <originatingIp>1.2.3.4</originatingIp> </LJAuthenticate> </soapenv:Body> </soapenv:Envelope> </syntaxhighlight>
- Response
- SSO SOAP Response expected by the Platform is as follows:
- <syntaxhighlight lang="xml" enclose="div">
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soapenv:Body> <LJAuthenticateResponse xmlns="urn:authentication.soap.ws.longjump.com"> <Status>Authenticated</Status> </LJAuthenticateResponse> </soapenv:Body> </soapenv:Envelope> </syntaxhighlight>
SAML
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML based standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between security domains. The Service Provider must enroll with an Identity Provider (IdP) and obtain an Issuer URL.
Working with SAML
An enterprise application contains a link to the AgileApps Cloud platform. When a user who has logged on to the enterprise platform clicks the link, he can automatically log in to the AgileApps Cloud platform without any additional authentication. For example, if an employee who has logged on the ABC Company corporate website clicks the link to the AgileApps Cloud platform on the landing page, he can log on to the AgileApps Cloud platform automatically without a second log in.
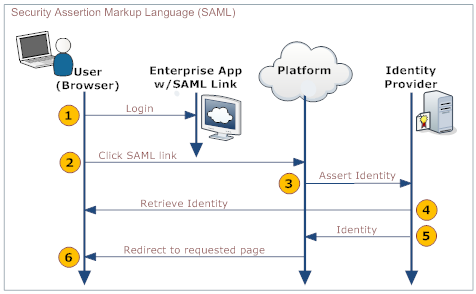
The following diagram explains the process:
User Your organization's web application Platform IdP 1. Log in to a web application provided by your organization - Provides a link to the platform's SAML handler (generated by the platform when SAML is configured)
- Includes the desired platform target page as an argument in the link
2. Click the link that directs to the SAML handler 3. Send an assertion to the IdP 4. Retrieve and validate the user's identity 5. Send the user's identity to the platform 6. Redirect the user to the appropriate page
Enabling SAML
- Click
 > Administration > Account Management > Single Sign-On Settings.
> Administration > Account Management > Single Sign-On Settings. - Click the [Edit] button.
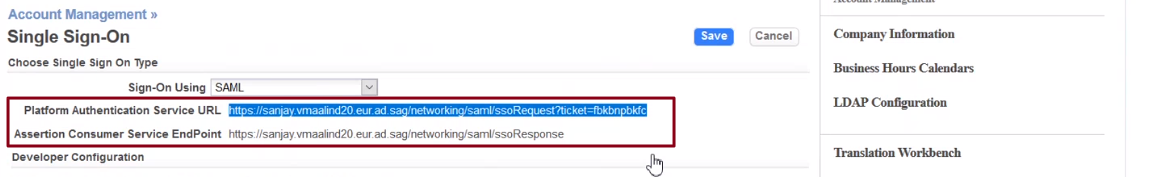
- Choose SAML from the Single Sign-On Using drop-down list. Selecting SAML automatically displays the Platform Authentication Service URL and the Assertion Consumer Service EndPoint fields below the drop-down list.
- Fill in the SAML Settings.
- Click [Save].
SAML Settings
- Platform Authentication Service URL
- To start the SAML authentication flow, copy this URL into your browser's address bar.
- Assertion Consumer Service Endpoint
- This URL needs to be configured in your Identity provider.
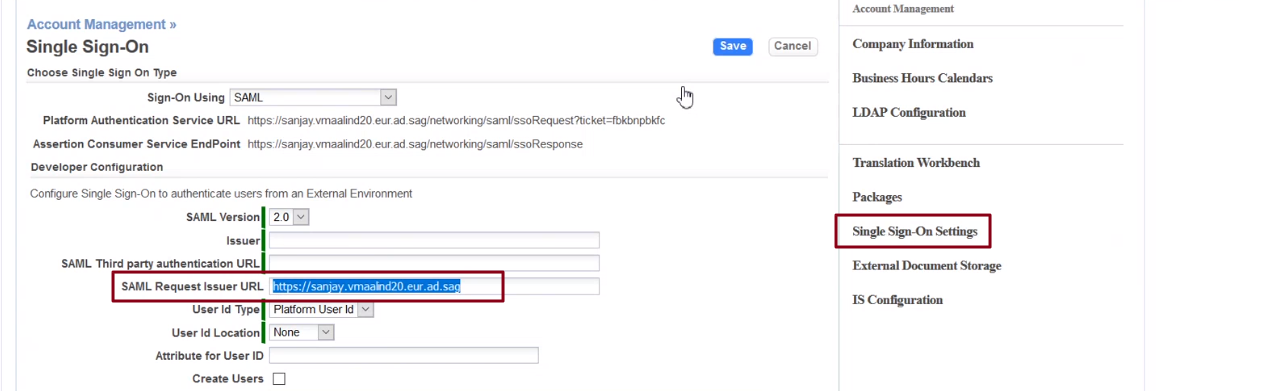
- SAML Version
- The default SAML version is 2.0
- Issuer
- This field contains the IdP's URL. After configuring the IdP for the tenant, copy the URL and paste it in this field. This URL is the SAML-response-issuer-URL.
- SAML Third Party authentication URL
- This field contains a URL (IdP single sign-on URL) which is used to authenticate a user or maintain a user's credentials. You might want to configure the IdP before you fill this field.
- Syntax:The URL and Port Number must be specified using a FQDN or an IP address, for example:
- www.abc.com:9090
- 192.168.1.10
- abc.def.com
- SAML Request Issuer URL
- This field contains a unique value which identifies the service provider, for example: http://yourCompany.agileappscloud.com.
- User Id Type
- Determines the type of identifier.
- Choose either Platform User Id or Federated Id.
- Platform User Id is the username of the user that is logged in, while Federated Id acts as the user's authentication across multiple IT systems or organizations.
- For more information on Federated ID, see Federated Identity.
- User Id Location
- Specifies an attribute tag that defines the location of the User Id.
- Choose either Subject or Attribute.
- Attribute for User ID
- Specify the IdP attribute that contains a platform User ID.
- If the User ID attribute is empty or does not match an existing user, either login fails or AgileApps creates a new user based on the Create Users flag.
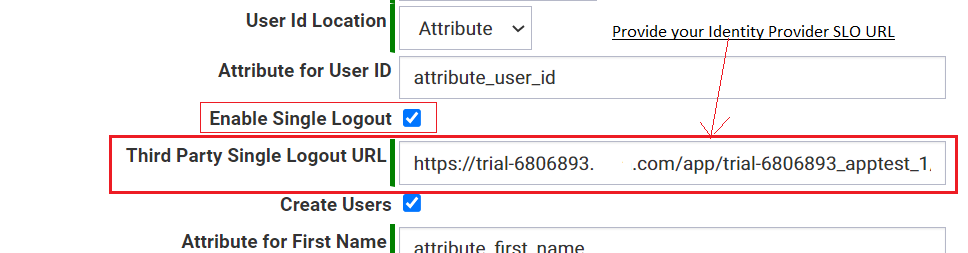
- Enable Single Logout
- Enable this if you want to provide Single Logout for the users.
- Third Party Single Logout URL
- You must provide the Single Logout URL provided by the Identity Provider.
- Logout Method
- Configure the logout method based on the support provided by the IDP. There are two logout methods available:
- Front-Channel Logout: When a user clicks on the logout option available on the Dashboard or Configuration pages, this method utilizes browser support to forward single logout requests and receive logout responses from the IDP. The Http-Post binding method is adopted for the front-channel method.
- Back-Channel Logout: This method is adopted for session management capability. When a user chooses to perform a logout from the SSO session in the session list, the AgileApps server sends a logout request to the IDP through the SOAP binding method. If session limit is reached for SSO sessions, the default and only applicable option is to "Auto logout the oldest session".
Check out the below possible scenarios for SSO and SLO with session management capability enabled.
SLO setting Session limit setting Behavior SLO OFF Session limit OFF Only AgileApps session logout. Users can log in with any number of sessions. SLO OFF Session limit ON The number of active AgileApps sessions is limited based on the session limit count value. When the session limit is reached, the oldest session of the user will be logged out. SLO ON
(Front Channel)Session limit OFF No session limit. Only AgileApps session logout is applicable. SLO ON
(Back Channel)Session limit OFF No session limit. Both IDP logout and AgileApps session logout are applicable. SLO ON
(Front Channel)Session limit ON The number of active AgileApps sessions limited is based on the session limit count value. When the session limit is reached, the oldest AgileApps session (not IDP session) of the user will be logged out. Choosing "Logout All" will perform only session logout from AgileApps (not IDP session). SLO ON
(Back Channel)Session limit ON The number of active AgileApps sessions limited is based on the session limit count value. When the limit is reached, both IDP logout and AgileApps session logout for the oldest session are applicable. Choosing "Logout All" will log out all IDP sessions and AgileApps sessions.
- Create Users
- Check this box to create a new user if AgileApps does not recognize the User ID.
- Attribute for First Name - The name of the SAML attribute that designates the user's first name.
- Attribute for Last Name - The name of the SAML attribute that designates the user's last name.
- Attribute for Email - The name of the SAML attribute that designates the user's email address.
- Default User Type - This field is used to specify the type of the user to be created.
- Choose either Platform User or Site User. The platform users are regular users in the platform while the site users have the similar behavior as portal users in the platform.
- When Site User is selected as the Default User in this SAML-SSO screen
- a. Only the Default Team is used for user creation. Other settings like default access profile, default application, and default role will be ignored.
- b. The created users will have same default settings as Access Profile (Portal User Profile) and Primary Team (Portal Users and Customers). Meanwhile, the user will also be a member of selected team in Default Team field (or any valid team-name provided through SAML attribute in ‘Attribute for Team’ field).
- Attribute for User Type- This field is used to specify the user-type to be created through SAML attribute. It is SITE for Site User and PLATFORM for Platform User. You might want to send the value for this attribute in the SAML response from the IdP.
- Default Team - This field is used to specify the default Team for the created user. For site users, the team will be a non-primary team.
- Attribute for Team- The name of the SAML attribute that designates the user's default team. For site users, the team will be a non-primary team.
- The attribute should contain a team name.
- Default Access Profile - This field is used to specify the default Access Profile for the created user. It is applicable only for Platform users.
- Attribute for Access Profile - The name of the SAML attribute that designates the user's access profile. It is applicable only for Platform Users.
- The attribute must contain an access profile's record ID.
- To get a record ID:
- a. Go to GearIcon.png > Access Management > Access Profiles.
- b. Modify the view to display Record ID, and copy the one you need.
- Default Application - This field is used to specify the default Application for the created user. It is applicable only for Platform users.
- This setting can be changed in the platform after user login.
- The user can change it in their Personal Settings. The admin can do the same in the Users page.
- To grant access to additional applications:
- a. A user record is created for the user in the platform after login.
- b. Use the Application Access page to specify the applications the user can access.
- Attribute for Application - The name of the SAML attribute that designates the user's application. It is applicable only for Platform users.
- The attribute should contain the application's name.
- Default Role - This field is used to specify the default Role for the created user. It is applicable only for Platform users.
- A user record is created for the user in the platform after login.
- The user can change it in their Personal Settings. The admin can do the same in the Users page.
- You can select multiple roles in this field.
- Attribute for Role - The name of the SAML attribute that designates the user's role in the application. It is applicable only for Platform users.
- This field can contain multiple role names separated by _::_
- For example, Agent_::_Manager
- Issuer Certificate
- Issuer certificate is used to sign and verify SAML messages. The certificate should be a valid x509 issuer certificate.
- Choose one of the following options:
- Navigate to the Issuer Certificate section, then select and load a file containing the Issuer Certificate (recommended)
- Paste the Issuer Certificate in the text area
User sync via SSO (SAML)
Overview
AgileApps now supports synchronizing user detail changes from identity providers. The following attributes are now synchronized:
- User basic information
- First name
- Last Name
- Email address
- Single or multiple Team updates in identity provider.
- Single or multiple role updates in identity provider.
Role and Team Sync
- For the user sync to function properly, the role and team should be delimited with the following character set _::_
Note:
- User sync is applicable only when Create User checkbox is enabled.
- Multiple team synchronization is supported through team attributes. However, a single team can be selected as default team in UI.
- User Sync will only be applicable for the users created through SSO flow, and not for the users created with REST API or UI flow.
- The primary team for the SSO Site users should always be Portal Users and Customers and the remaining teams will be assigned as secondary teams.
- Roles will not be synchronized for the SSO Site users.
- For SSO Platform users the first team provided in the SAML response will become the primary team, and the remaining teams will be assigned as secondary teams.
- During the user creation, the default User Type, Role, Team, Application and Access Profile are considered if
- The corresponding Attributes for the fields are empty or
- The value of the attribute is empty from the identity provider or
- The system does not find the corresponding value into the System database.
- The user sync for Teams and Roles will follow an override approach. The existing teams or roles for this user will be removed and the new teams / roles will be added which are provided as value in the corresponding attributes from Identity Provider.
- User sync will not succeed if the provided teams or roles in SAML attributes, do not exist in AgileApps.
- In these circumstances when user sync fails, open the browser's console and look for the response header SSOErrorMessage in order to analyze the fault.
Using SAML
To use single sign-on with SAML, create links that directs you to the platform's SAML handler and pass the desired destination page as an argument.
To create a link to the platform in your enterprise application:
- Copy the SAML link generated as the Platform Authentication Service URL while configuring SAML
- Add a done= argument to the link that specifies the target page in the platform
To create the done= argument:
- Go to the standard initial page using <syntaxhighlight lang="java" enclose="div"> servicedesk/index.jsp </syntaxhighlight>
- Go to the page that you want to target.
- Copy the URL from the browser's address bar.
- For old UI, edit the URL to remove <syntaxhighlight lang="java" enclose="div"> https://{yourDomain}/networking/ </syntaxhighlight>
Add the remaining as the value for done= parameter.
- For example: servicedesk/index.jsp#_a87199395ac14d01b3402a7915c0ff78/245418134 or pages/TestPage.jsp
- URL encode the link
- For more information, see URL Encoding.
So, the complete URL used to access AgileApps through SSO would look like:
- Old UI: <syntaxhighlight lang="java" enclose="div"> https://{serviceDomain}/networking/saml/ssoRequest?ticket=cnpkkccqsqscnp&done=servicedesk%2Findex.jsp%23_a87199395ac14d01b3402a7915c0ff78%2F245418134 </syntaxhighlight>
- New UI: <syntaxhighlight lang="java" enclose="div"> https://{serviceDomain}/networking/saml/ssoRequest?ticket=cnpkkccqsqscnp&done=https%3A%2F%2F{serviceDomain}%2Fagileapps%2Frecords%2Fdetail%2Fcases%2F558782450 </syntaxhighlight>
Important Notes
- AgileApps supports authentication for Platform Users and Site Users through any IdP like Azure AD, OKTA, OAM, PING, and so on
- If the user doesn't exist in AgileApps, a new user can be created by selecting Create Users check box and configuring the AgileApps-SSO-SAML screen
- AgileApps has an option for creating Platform Users and Site Users using the pre-stored attributes or parameters in the IdP
- Any unique name or ID provided as an attribute value in the 'Attribute for User ID' field in AgileApps-SSO screen is the username of the newly created user
- Any Attribute value sent from the IdP should contain Names instead of IDs, for example, Application Name, Team Name, Access Profile Name, and Role Name
- The default field value in SSO screen will be overridden with the corresponding attribute values if a valid attribute value is provided through the IdP
- First Name, Last Name, Email, and Username fields are read-only fields for the users created in AgileApps through SSO-SAML because the IdP will only be the source of identity for such users, hence these identification must not be modified from any other source except the IdP.
Note: The basic user information is synchronized during the login process through SSO. For more details, see User sync via SSO (SAML)
- The users created in AgileApps through SSO cannot reset their password
Pass Through Authentication
Pass Through Authentication (PTA) lets a user go straight to the platform from an organization's web page or application, without having to log in again.
Working with pass through authentication
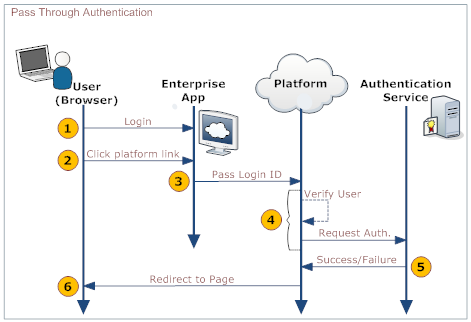
After logging on to an enterprise application, you might want to visit a page hosted on the platform without logging on to that platform. A single log on to the enterprise application gives you access to all the pages hosted on the platform. The application sends a SOAP message to the platform in an HTTP request. That SOAP message contains the information needed to log on to the platform. The data in it is passed to an authentication server which sends back a message saying whether the authentication has succeeded or failed. The user is directed to the appropriate page, as displayed in the following diagram:
Here is an explanation of the steps:
User Your organization's web application Platform Authentication server 1. Log on to a web page or application provided of your organization 2. Click a link that directs to a platform page 3. Pass data to the platform's PTA service in the SOAP payload - Session ID (optional, but desirable)
- Login ID
4. - Receive data in the SOAP payload:
- Pass data to the Authentication server
5. - Authenticate the user
- Send back a success-report or failure-report
6. Redirect the user to the appropriate page.
Enabling Pass Through Authentication
The URL of the Authentication Server and the URLs of the pages to visit in the event of success or failure are configured in the platform's Single Sign-On Settings:
- Click
 > Administration > Account Management > Single Sign-On Settings.
> Administration > Account Management > Single Sign-On Settings. - Click the [Edit] button.
- Choose Pass Through Authentication from the Single Sign-On Using drop-down list. Selecting Pass Through Authentication automatically displays the Platform Authentication Service URL field below the drop-down list.
- Specify the location of the authentication service in the Third party Authentication Service URL field. The platform uses this URL to authenticate the USER and pass the appropriate pay load in the HTTP request.
- Enter the URL of the page where you want to go when the authentication succeeds in the “Success page URL” field.
- If the URL is not specified then the platform will take you to the home page.
- Enter the URL of the page where you want to go when the authentication fails in the “Error page URL” field.
- If the URL is not specified then the platform will take you to the login page.
- This field can be overridden dynamically by the Authentication Server
- Click [Save]
Message Formats
Posting a Form to the Platform
The following is an example of a form which the application or web page uses to make an HTTP POST to the platform. The user is then seamlessly redirected to the success or failure page depending on the authentication.
- <syntaxhighlight lang="xml" enclose="div">
<form id='testForm'
action='https://{yourDomain}/networking/passThroughAuth' METHOD="POST" enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
>
<input type="hidden" name="loginID" value="jondoe@test.com"> <input type="hidden" name="sessionID" value="adasd3qw4q4weasdasd">
</form> </syntaxhighlight>
Where,
- loginID
- The user's login name on the platform, typically in the form of an email address.
- sessionID
- The session ID of the user on the organization's website. This field is optional. It is passed on to the authentication service, so the authentication service can make use of it.
When the platform receives POSTed form data, it passes the data to the Authentication Service using content type application/x-www-form-urlencoded, in a request. See the example below:
- Method
- POST
- URI
- Configured in the Single Sign-On Settings
- Content-Type
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- Payload
- A URL Encoded version of a data string that looks like this:
- <syntaxhighlight lang="text" enclose="div">
loginID=jondoe@test.com&sessionID=adasd3qw4q4weasdasd </syntaxhighlight>
- The Authentication Service reads the identification parameters from the request as it is in this Java code, for example:
- <syntaxhighlight lang="java" enclose="div">
String loginId = (String)request.getParameter("loginID"); String sessionId = (String)request.getParameter("sessionID"); </syntaxhighlight>
Where request is the object containing the HTTP request (for example, in an HttpServlet instance).
Sending a SOAP Request to the Platform
This message format can be delivered to the platform by an application or web page.
- Method
- POST
- URI
- https://{yourDomain}/networking/passThroughAuth
- <syntaxhighlight lang="xml" enclose="div">
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<soapenv:Body>
<LJAuthenticate xmlns="urn:authentication.soap.ws.longjump.com">
<sessionID>...</sessionID>
<loginID>...</loginID>
</LJAuthenticate>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope> </syntaxhighlight>
Where:
- sessionID
- The session ID of the user on the organization's website. Optional. It is passed on to the authentication service, so the authentication service can make use of it.
- loginID
- The user's login name on the platform--typically in the form of an email address.
When the platform receives a SOAP request, it sends a message in the following format to the Authentication Server:
- Method
- POST
- URI
- Configured in the Single Sign-On Settings
- <syntaxhighlight lang="xml" enclose="div">
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<soapenv:Body>
<LJAuthenticate xmlns="urn:authentication.soap.ws.longjump.com">
<sessionID>...</sessionID>
<originatingDomain>...</originatingDomain>
<originatingIp>...</originatingIp>
<loginID>...</loginID>
</LJAuthenticate>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope> </syntaxhighlight>
- Where:
- originatingDomain
- Name of the Domain the request originally came from (e.g. wwww.paaspartout.com)
- originatingIp
- IP Address of the domain the request originally came from (e.g. 10.20.30.40)
- sessionID
- Passed on from the original request
- loginID
- Passed on from the original request
Messages Returned by the Authentication Server
After authenticating the user, the server sends back a success or failure response.
- Authentication-Succeeded response
- This response is sent when authentication succeeds.
- <syntaxhighlight lang="xml" enclose="div">
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<soapenv:Body>
<LJAuthenticateResponse xmlns="urn:authentication.soap.ws.longjump.com">
<status>AUTHENTICATED</status>
<loginID>userLogin@Login.com</loginID>
</LJAuthenticateResponse>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope> </syntaxhighlight>
- Authentication-Failed response
- This response is sent when authentication fails.
- <syntaxhighlight lang="xml" enclose="div">
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<soapenv:Body>
<LJAuthenticateResponse xmlns="urn:authentication.soap.ws.longjump.com">
<status>NOT_AUTHETICATED</status>
<loginID>userLogin@Login.com</loginID>
<redirectOnErrorURL>http://www.location.com/somePage</redirectOnErrorURL>
</LJAuthenticateResponse>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope> </syntaxhighlight>
- Where:
- redirectOnErrorURL
- URL of the next page the user sees. (Overrides the Single Sign-On settings.)