Difference between revisions of "Delegated Authentication"
imported>Aeric |
imported>Aeric |
||
| (25 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
With delegated authentication, you use your own server to validate platform Users against a corporate database or an LDAP Directory. Users can then use a single username and password to access all of their applications--as long as they support delegated authentication. | |||
===Scope === | |||
Delegated Authentication is limited to user authentication and does NOT include authorization. Users must be active in the platform. Teams, Roles and other permissions must also be maintained. | |||
It is the responsibility of the corporate System Administrator/IT Staff to develop and implement a Web service that can accept and respond to the web service calls made by the platform servers. | |||
===How Delegated Authentication Works=== | |||
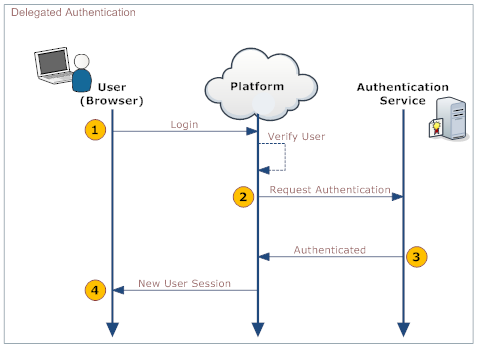
When a User logs in, their identity is authenticated in both the platform and in your organization's systems. The following diagram shows the process: | |||
:[[File:SSO-DA.png]] | |||
This table describes the actions taken by the User, the platform, and your organization's [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_service Web Service]. | |||
{| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" | :{| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" | ||
!User | ! | ||
!Platform | !User | ||
!Your Organization's Web Service | !Platform | ||
!Your Organization's Web Service | |||
|- | |- | ||
|1. | |1. || Log into the platform || Validate that: | ||
:* User is Active | :* User is Active | ||
:* SSO is Enabled | :* SSO is Enabled | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
|2. ||Make a Web Services call to the organization's | |2. || || Make a Web Services call to the organization's Web service, requesting authorization. | ||
Web service, requesting authorization. Include | Include these parameters in the call: | ||
these | :<syntaxhighlight lang="java" enclose="div"> | ||
username | |||
password | |||
originatingIp | |||
Note: originatingIp is the IP address that originated the login request. This could be useful to restrict access based on the user’s location. The Web Service must be implemented in a way that the platform is able to access it. | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
''Note:'' originatingIp is the IP address that originated the login request. This could be useful to restrict access based on the user’s location. The Web Service must be implemented in a way that the platform is able to access it. | |||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
|3. || ||Validate the passed information and return either "Authenticated" or "Failure". | |3. || || || Validate the passed information and return either "Authenticated" or "Failure". | ||
|- | |- | ||
|4. ||On Authenticated response, generate a new User Session. On Failure, notify the user.|| | |4. || || On Authenticated response, generate a new User Session. On Failure, notify the user.|| | ||
|} | |} | ||
====Making a Web Service Call | ===Enabling Delegated Authentication=== | ||
#Click '''Settings > Administration > Single Sign-On''' | |||
#Click the '''[Edit]''' button | |||
#For ''Single Sign-On Settings'', choose '''Delegated Authentication''' | |||
#Fill in the Delegated Authentication Settings: | |||
#*Specify the URL of the authentication server running in your environment (abc5.abc.com:8080) | |||
#:Note that the URL and Port number must be specified using a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FQDN Fully Qualified Domain Name] or an IP address. Secure HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer) protocol is used to access this URL. | |||
#:''If you do not have this information available, contact your IT department or System Administrator.'' | |||
#*Choose whether or not to Enable Single Sign-On for individual [[User]]s. | |||
#Click '''[Save]''' | |||
===Setting up Communications with the Authentication Server=== | |||
For a successful handshake with the platform, the authentication server needs a certificate. If you are using a self-signed certificate, it needs to be loaded into the cacert keystore file in the platform's <tt>{installed_JDK}/jre/lib/security</tt> folder. Otherwise, you get an SSL error. | |||
To load the certificate into the keystore: | |||
# Make sure that the <tt>JAVA_HOME</tt> environment variable points to the JRE in an installed JDK.<br/>Check the configuration in these three locations: | |||
#:* <tt>installation.properties</tt> | |||
#:* <tt>configure.pl</tt> installation script | |||
#:* <tt>scripts/longjump</tt> | |||
#: ''Learn more:'' Platform [[Installation Files]] | |||
# Load the certificate using the <tt>keytool -import</tt> command/ | |||
#: The default password is "changeit". | |||
#: ''Learn more:'' [http://download.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/security/toolsign/rstep2.html Java Tutorial: Importing a Certificate] | |||
===Making a Web Service Call=== | |||
Use the URL and port number provided under the ''Single Sign-On Settings'' Section to make a SOAP request to authenticate the users. SSO Request and SSO Response are predefined by the platform. These request and response are conducted via SOAP messaging. | Use the URL and port number provided under the ''Single Sign-On Settings'' Section to make a SOAP request to authenticate the users. SSO Request and SSO Response are predefined by the platform. These request and response are conducted via SOAP messaging. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 68: | ||
===Web Services Message Format=== | ===Web Services Message Format=== | ||
;Request:SSO SOAP Request sent from the platform is as follows: | ;Request:SSO SOAP Request sent from the platform is as follows: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="xml" enclose="div"> | :<syntaxhighlight lang="xml" enclose="div"> | ||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> | ||
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> | <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> | ||
| Line 69: | Line 82: | ||
;Response:SSO SOAP Response expected by the Platform is as follows: | ;Response:SSO SOAP Response expected by the Platform is as follows: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="xml" enclose="div"> | :<syntaxhighlight lang="xml" enclose="div"> | ||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> | ||
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> | <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> | ||
| Line 79: | Line 92: | ||
</soapenv:Envelope> | </soapenv:Envelope> | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:58, 19 September 2012
With delegated authentication, you use your own server to validate platform Users against a corporate database or an LDAP Directory. Users can then use a single username and password to access all of their applications--as long as they support delegated authentication.
Scope
Delegated Authentication is limited to user authentication and does NOT include authorization. Users must be active in the platform. Teams, Roles and other permissions must also be maintained.
It is the responsibility of the corporate System Administrator/IT Staff to develop and implement a Web service that can accept and respond to the web service calls made by the platform servers.
How Delegated Authentication Works
When a User logs in, their identity is authenticated in both the platform and in your organization's systems. The following diagram shows the process:
This table describes the actions taken by the User, the platform, and your organization's Web Service.
User Platform Your Organization's Web Service 1. Log into the platform Validate that: - User is Active
- SSO is Enabled
2. Make a Web Services call to the organization's Web service, requesting authorization. Include these parameters in the call:
username password originatingIp
Note: originatingIp is the IP address that originated the login request. This could be useful to restrict access based on the user’s location. The Web Service must be implemented in a way that the platform is able to access it.
3. Validate the passed information and return either "Authenticated" or "Failure". 4. On Authenticated response, generate a new User Session. On Failure, notify the user.
Enabling Delegated Authentication
- Click Settings > Administration > Single Sign-On
- Click the [Edit] button
- For Single Sign-On Settings, choose Delegated Authentication
- Fill in the Delegated Authentication Settings:
- Specify the URL of the authentication server running in your environment (abc5.abc.com:8080)
- Note that the URL and Port number must be specified using a Fully Qualified Domain Name or an IP address. Secure HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer) protocol is used to access this URL.
- If you do not have this information available, contact your IT department or System Administrator.
- Choose whether or not to Enable Single Sign-On for individual Users.
- Click [Save]
Setting up Communications with the Authentication Server
For a successful handshake with the platform, the authentication server needs a certificate. If you are using a self-signed certificate, it needs to be loaded into the cacert keystore file in the platform's {installed_JDK}/jre/lib/security folder. Otherwise, you get an SSL error.
To load the certificate into the keystore:
- Make sure that the JAVA_HOME environment variable points to the JRE in an installed JDK.
Check the configuration in these three locations:- installation.properties
- configure.pl installation script
- scripts/longjump
- Learn more: Platform Installation Files
- Load the certificate using the keytool -import command/
- The default password is "changeit".
- Learn more: Java Tutorial: Importing a Certificate
Making a Web Service Call
Use the URL and port number provided under the Single Sign-On Settings Section to make a SOAP request to authenticate the users. SSO Request and SSO Response are predefined by the platform. These request and response are conducted via SOAP messaging.
Web Services Message Format
- Request
- SSO SOAP Request sent from the platform is as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soapenv:Body> <LJAuthenticate xmlns="urn:authentication.soap.ws.longjump.com"> <username>jim@abc.com</username> <password>sales</password> <originatingIp>1.2.3.4</originatingIp> </LJAuthenticate> </soapenv:Body> </soapenv:Envelope>
- Response
- SSO SOAP Response expected by the Platform is as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soapenv:Body> <LJAuthenticateResponse xmlns="urn:authentication.soap.ws.longjump.com"> <Status>Authenticated</Status> </LJAuthenticateResponse> </soapenv:Body> </soapenv:Envelope>