The Power of Objects
About Objects
Objects lie at the core of a data model. They define the primary information structure, with rows and columns of data (like a spreadsheet), but they also contain many additional capacities that support nimble applications:
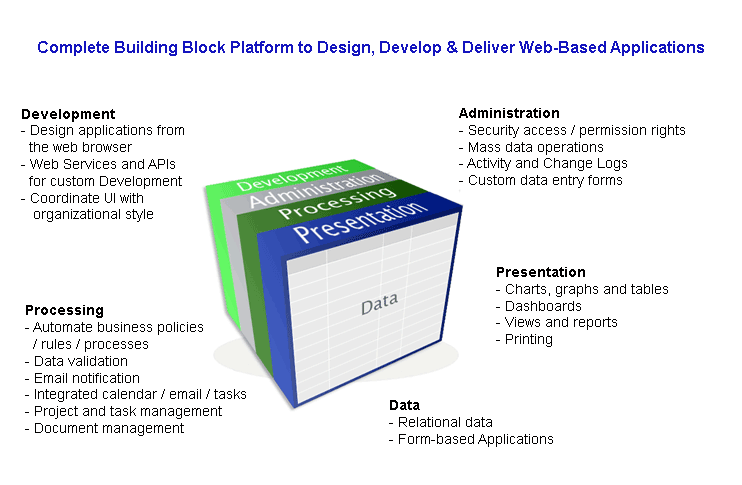
Presentation
- Display custom forms for manual data entry
- Present data as charts, graphs, tables for display or print
- Display dashboards: high-level status updates in real-time
Processing
- Interface to external systems (import/export)
- Model business policies/rules/processes that match the needs of your organization
- Validate data for improved accuracy
- Improve staff time management with email notifications and task-based activities via an integrated calendaring system
- Build data relationships
Administration
- Define security permissions and access control for users/teams/roles
- Manage mass data operations
- Monitor activity and change logs
- Design data entry forms, views and reports that are personalized to the needs of the users/teams/roles
Development
- Use the web browser-based IDE to design objects and applications
- Design fully customized objects and applications with the APIs and Web Services tools
- Design a UI to coordinate with organizational style guides
Customizing Objects
Automating Objects
You can define automated Data Policies that take actions you desire under conditions you specify, and you can specify Workflows to move a record from person to person, across departments--using Roles to define job responsibilities, so anyone with that role can do the processing needed in the next step.
Objects and Object Relationships
Objects are powerful in an of themselves, but they derive even greater power from the Object Relationships you can create to tie them together.
When you combine that capability with the capacity for automated data policies and workflows, the result is a high degree of automation with a minimal amount of work.