Difference between revisions of "Expressions"
imported>Aeric |
imported>Aeric |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ | |||
==About Expressions== | |||
{{:Introduction to Expressions}} | {{:Introduction to Expressions}} | ||
== Filter Expressions | == Filter Expressions == | ||
{{:Filter Expressions | {{:Filter Expressions}} | ||
==Formula Expressions== | ==Formula Expressions== | ||
{{:Formula Expressions}} | {{:Formula Expressions}} | ||
Latest revision as of 22:58, 9 May 2014
About Expressions
An expression is any valid set of literals, variables and operators that evaluates to a single value.
An expression is used to build Filter criteria or a Formula.
Two different kinds expressions are used in the platform:
- Filter Expressions
- Used to select records.
- The value of the expression is always a Boolean (true or false) value.
- Expressions are created using fields, values, comparison operators, and logical operators.
- Fields in the object record can be referenced.
- Filter expressions do not include functions.
- Formula Expressions
- Used to return a value.
- The resulting value can be a number, a string, a date/time, or a Boolean (Logical: TRUE/FALSE).
- A wide variety of Formula Functions are available.
For example:
- ROUND( amount * 0.02, 2) (rounds the variable to the nearest 2 decimal places)
- Fields in the object record and in Lookup target records can be referenced, up to 5 levels deep.
- Logical operations are performed using functions AND() and OR()
The simplest expression is a literal value, a variable, or a formula function:
- 972 (a numeric literal)
- 'Steve' (a string literal)
- creation_date (a variable value)
- TODAY (a formula function that returns the current date)
More complex expressions are created by combining values with operators. For example:
- amount * 0.02
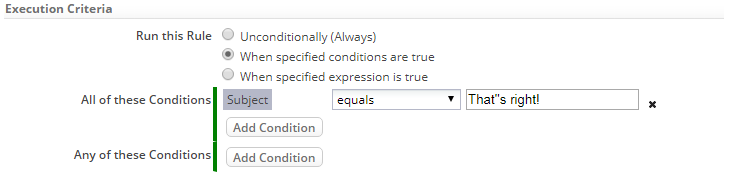
Filter Expressions
About Filter Expressions
A filter expression is a special type of expression that is used to search for records. Filter expressions are used in:
- Views
- Report Filters
- Lookup Filters
- Developer APIs
- JAVA APIs
- REST APIs (Also used for AJAX and REST.)
The Filter Expression Builder is used to define an expression, using a combination of fields, values, comparison operators, and logical operators. The resulting expression is used to evaluate a group of records. Records that match the specified criteria are returned.
Building Filter Expressions
Components of a filter expression are: <FIELD_NAME> <COMPARISION_OPERATOR> <VALUE> <LOGICAL_OPERATOR>
FIELD_NAME
The name of the Field or Computed Field to use in creating a filter.
COMPARISON OPERATOR
- The following operators are available in a filter expression:
Operator Description equals Returns only records with the specified value not equal to Returns only records that do not include the specified value less than Returns only records that are less than the specified value less than equals Returns only records that are less than or equal to the specified value greater than Returns only records that are more than the specified value greater than equals Returns only records that are more than or equal to the specified value contains Returns only records that contain the specified value not contains Returns only records that do not contain the specified value starts with Returns only records that start with the specified value ends with Returns only records that end with the specified value
FIELD_VALUE
- The search value - a string, a date, a number.
- Examples:
- String: 'Paper 123'
- Date: '06/06/2007'
- Numeric Value: 9383
- Empty Field: '' or BLANK
- Follow these guidelines when specifying values:
- The value can be partial text or whole words
- Enclose strings and date/time values in 'single quotes'
- To specify date values, use the Date Format as specified in Company Information
- To search for a blank (empty) string, use two single quotes, with nothing between them ('').
- To search for a blank (empty) field of other kinds, use a field value of BLANK
- To search for multiple field values, separate each value using vertical pipe (|)
- For example: company_name='Acme|Ajax'
- (The criteria is satisfied when the company name is either Acme or Ajax)
- To search for a field value that happens to contain a vertical pipe (|), you need to "escape" the pipe so it is recognized as a literal character in the field. To do that, you put a backslash in front of it: \|. For example, company_name contains '\|'
- That works in REST APIs and in the GUI.
- In Java strings, the backslash is already an escape character. (It combines with the one that follows it to create a single character.)
- So in Java code, you need two backslashes: \\|
- (The first two (\\) combine to become a single backslash (\), so the filter expression handler sees "\|", as desired.)
- Finally, note that "equals" does not work for this particular search. The required operator is "contains".
- To include a single quote in the value that you are searching for, specify an additional quote for every single quote ('').
LOGICAL_OPERATOR
- Logical operators can be used to build more complex expressions.
- The logical operators are:
- AND
- OR
- Considerations
-
- Two subexpressions joined by a logical operator form a logical expression.
- Logical expressions resolve to a Boolean value: 1/0 or TRUE/FALSE.
- Use parentheses--()--to group expressions logically and to join multiple expressions.
- Parentheses are used in pairs; each open parenthesis "(" requires a closing parenthesis ")".
- For example:
- ((<expression1> AND <expression2>) OR (<expression3> AND <expression_4>))
- Learn more: Using Logical Operators and Parentheses
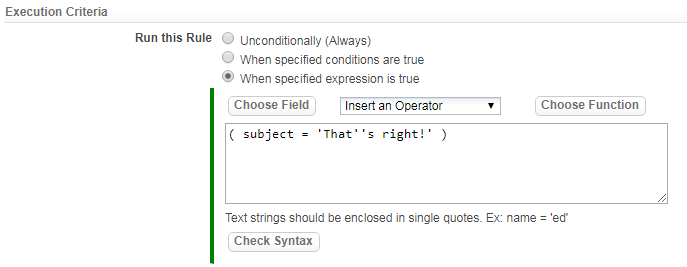
Formula Expressions
About Formula Expressions
Formula expressions give you the ability to calculate dynamic values and apply dynamically-generated criteria to a search.
Formula expressions are used in these areas of the platform:
- Computed Fields in Reports
- Default Field Values
- Formula Fields
- Layout Rule#Settings
- Macro Visibility Criteria
- Rule Execution Criteria
- Rule Actions to add or update a record
- Validation Criteria
Building a Formula Expression
A formula expression is essentially equivalent to a spreadsheet formula. Formula expressions are built from fields, operators, functions, and values.
Typically, formula expressions are built using the buttons and drop down lists provided in the Formula Builder, but they need not be. A fully-formed expression can simply be typed or pasted into the builder's expression-box text area.
Values
- A number, date, or string you enter into the expression:
- A string or date needs to be enclosed in single quotes. For example: 'ABC Company'.
- You specify an empty string using two single quotes with nothing between them: ''
Fields
- The name of an object Field, a Computed Field, or a Referential Field (to reference a field in a related object).
Functions
- One of the built-in Formula Functions. Functions can nest to arbitrary depth.
- For example, to create a conditional expression, start by selecting the logical IF function from the drop down (which gives you a template), or else type in the conditional expression in a format like this:
- IF (test, value-if-true, value-if-false)
Note:
Unlike Filter Expressions, and/or logic in a Formula Expression is added using the functions AND(boolean_expression_1, boolean_expression_2) and OR(boolean_expression_1, boolean_expression_2).- Learn more: Formula Functions#Logical Functions
Operators
- Available operators are:
Operator Name Description Examples != Not Equal Evaluates if two numbers/strings/boolean values are not equal in value, and returns TRUE if the numbers/strings/boolean values are not equal Is the listed price not equal to $100? - Listed_Price != $100
&& Logical AND Compares two Logical Boolean expressions, and returns TRUE if both conditions are TRUE Is the total amount greater than $10,000 and the requested delivery date in the future? - total_amount > 10000 && delivery_date > TODAY (NOW())
> Greater Than Evaluates if a number is greater than another number, and returns TRUE if the condition is met Are sales greater than the quota of $10,000/month? - Quota> 10000
>= Greater Than or Equal To Evaluates if a number is greater than or equal to another number, and returns TRUE if the condition is met Are sales greater than or equal to the quota of $10,000/month? - Quota>= 10000
< Less Than Evaluates if a number is less than another number, and returns TRUE if the condition is met Are sales less than the quota of $10,000/month? - Quota< 10000
<= Less Than or Equal To Evaluates if a number is less than or equal to another number, and returns TRUE if the condition is met Are sales less than or equal to the quota of $10,000/month? - Quota<= 10000
( ) Parentheses or Brackets Creates groups of expressions Evaluates the expressions between the open and closed brackets before evaluating the parts of the expression outside of the brackets
Multiply the price by the number of units, then apply a discount to the resulting value - (Number_of_Units * Price) - Discount
* Multiply Multiplies two numbers Multiply the total amount due by a discount amount - Total_Due * Discount_%
+ Plus or Concatenate Has two functions:
- Calculates the sum of two numbers
- Joins multiple text strings into one text string
- Returns the sum of the tax and shipping:
- (SubTotal * Tax) + Shipping
- Creates a value formatted for Sorting (by last name)
- LASTNAME + ', ' + FIRSTNAME
- Minus Calculates the difference between two numbers Calculate the number of units yet to be delivered - Quantity_Ordered - Quantity_Received
/ Divide Divides a number by another number Divide a yearly sales quota by 12 to find a monthly quota amount - Quota/ 12
= Equal Evaluates if two numbers are equal in value, and returns TRUE if the condition is met Is the price equal to $100? - Price=$100
|| Logical OR Compares two Logical Boolean expressions, and returns: - TRUE if either of the conditions are TRUE
Is the total amount is greater than $10,000, or is the requested delivery date in the future? - total_amount > 10000 || delivery_date > TODAY (NOW())
Examples
Here are some examples of typical Formula Expressions.
Simple Formula Expressions
In a reservations application, there are fields for Creation Date, Check In Date, and Check Out Date. A formula field can calculate the number of days between the Creation Date and Check In Date. To create such a formula field, use the date fields and the DATECOMP formula function. DATECOMP will give a positive result when the later date is the first operand. It will give a negative result if the later date is the second operand.
| Formula Expression | Description |
|---|---|
| DATECOMP(check_in_date, creation_date) | Compare the future Check In Date and the reservation Creation Date, and return the difference in the number of days |
| DATECOMP(TODAY(), check_in_date) | To build a complex expression, nest the expressions. This example compares Today's Date to the Check In Date and returns the difference in the number of days. (TODAY returns the current date.) |
| IF((DATECOMP(check_in_date, TODAY())<2), 'Rush', 'Standard') | A more complex example uses the logical formula function IF to return one of two text results: 'Rush' if the Check In Date is less than two days from today, and 'Standard' if the Check In Date is two days or more away. |
Complex Formula Expressions
Examples of complex Expressions.
| Formula Expression | Description |
|---|---|
| age = (datesub (now(), DOB)) / 365.25 | calculates age, based on date of birth (DOB) |
| discount = (pre_discount_amount * (2.5 /100)) + total_amount | calculates a discounted price |
| IF(probability = 1, ROUND(amount * 0.02, 2), 0) | calculates the 2% commission amount of an opportunity that has a probability of 100%; all other opportunities have a commission value of zero. |
| SUBSTRING(phone, 2, 4) + SUBSTRING(phone, 7, 9) + SUBSTRING(phone, 11, 14) | removes the parentheses, spaces and dashes from a telephone number in the US format (xxx) xxx-xxxx |
| SUBSTRING(phone, 1, 3) + SUBSTRING(phone, 5, 7) + SUBSTRING(phone, 9, 12) | removes the dashes from a telephone number in the US format xxx-xxx-xxxx |
| IF((STARTSWITH(phone,'(')), (SUBSTRING(phone, 2, 4) + SUBSTRING(phone, 7,9) + SUBSTRING(phone, 11,14) ), (SUBSTRING(phone, 1,3) + SUBSTRING(phone, 5, 7) + SUBSTRING(phone, 9, 12)) ) | checks a telephone number to see if it starts with an open parenthesis and if so removes the parentheses, dashes and spaces; otherwise, the expression removes the dashes from the telephone number |
| IF(AND(IF(DATESUB(TODAY(), payment_due_date)>0, true,false), payment_status ='UNPAID'), 'PAYMENT OVERDUE', null) | determines if the payment due date is past and the payment status is "UNPAID"; if true, it returns "PAYMENT OVERDUE" and null otherwise |
| IF(OR(category!='IT', AND (category='IT', amount <3000)),true, false) | checks for a department (IT department) and amount less than $3000; returns TRUE if the department is not "IT"; also returns TRUE if the department is "IT" and the amount is less than $3000 |
| IF(AND(ISNEW(),IF(DATESUB(TODAY(), close_date)>0, true, false)), true, false) | checks new opportunities, returning TRUE if it has a close date that is in the future; returns FALSE if close date is in the past |
| IF(OR(priority='High', status='New'), ROUND(DATESUB(NOW(), created_date)), 0) | returns the number of days a case has been open if the status is new or the priority is high; returns zero otherwise |