Difference between revisions of "Cluster Deployment"
From AgileApps Support Wiki
imported>Aeric |
imported>Aeric |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<includeonly>===Prototype Deployment===</includeonly> | <includeonly>===Prototype Deployment===</includeonly> | ||
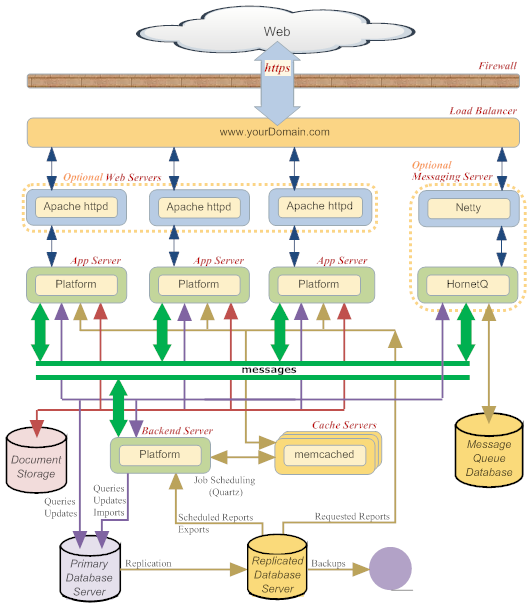
The following diagram shows the kind of architecture that is typical for a production system pre-10.3 release and post 10.3 release. With the 10.3 release, AgileApps uses the common Tomcat that comes along with the IS installation and does not use the stand-alone Tomcat anymore. This allows AgileApps access to the flow services on the co-hosted IS. | The following diagram shows the kind of architecture that is typical for a production system pre-10.3 release and post 10.3 release. With the 10.3 release, AgileApps uses the common Tomcat that comes along with the IS installation and does not use the stand-alone Tomcat anymore. This allows AgileApps access to the flow services on the co-hosted IS. The following images allow you to identify the difference in the architecture for pre and post 10.3 release. | ||
::::::::'''Architecture for pre-10.3 Release''' | ::::::::'''Architecture for pre-10.3 Release''' | ||
Revision as of 06:19, 13 December 2019
The following diagram shows the kind of architecture that is typical for a production system pre-10.3 release and post 10.3 release. With the 10.3 release, AgileApps uses the common Tomcat that comes along with the IS installation and does not use the stand-alone Tomcat anymore. This allows AgileApps access to the flow services on the co-hosted IS. The following images allow you to identify the difference in the architecture for pre and post 10.3 release.
- Architecture for post-10.3 Release
- Architecture for post-10.3 Release
The key points depicted in the diagram are:
- The platform is deployed across multiple servers.
- A Load Balancer distributes traffic across the web servers.
- Apache httpd is an optional front-end web server for the application server.
Learn more: Installing and Configuring Apache for Use with the Platform - The Messaging server handles all social media interactions .
It also handles on-screen notifications when people are looking at the same case.
- Messages are exchanged between it and the application server to manage those interactions.
- HornetQ maintains the store-and-forward message queue for those communications.
- Learn more: Installing the Messaging Server
- Memcached servers reduce response time by caching data in memory.
Learn more: Configuring memcached - The suite of memcached servers are accessed by all application servers, backend as well as front end.
- The critical backend processes shown here (import, export, and scheduling, which uses quartz) are all being run from a single platform instance. But additional servers can be employed, as load demands.
Learn more: Managing Backend Services - Document storage (which includes pictures and image files) is managed separately from the database.
- The database is running on its own server, for added performance.
Learn more: Configuring MySQL to Run on a Separate Server - The primary database instance and the replication instance are each running on separate servers, both for reliability and for performance of read-intensive operations.
Learn more:
- Using Replication with Different Master and Slave Storage Engines
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.5/en/replication-solutions-diffengines.html
- Requests that access and update, whether coming from a user or a backend process, go to the primary database, while read-intensive operations (backups, reports, exports) are executed on the replicated database.
Learn more: Running Reports and Storage Checks On a Replicated Database Server.