Quick Install Guide
Overview
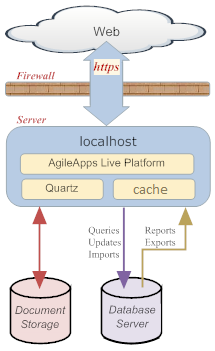
This guide is intended for installers who are setting up a version of the platform for application building and testing. A typlical deployment would look something like this:
Installation Components The key points depicted in the diagram are:
- The platform is deployed on a single server.
- Memcached reduces response time by caching data in memory.
Learn more: Configuring memcached - Ehcache reduces response time by caching data in memory.
Learn more: Configuring Ehcache - Background processes import, export, and the quartz scheduler are running on the same server.
- Document storage (which includes pictures and image files) is managed separately from the database.
- The database is running on the same server, for ease of deployment.
- The database is not replicated, as this deployment optimized for small-scale performance.
Additional Resources
- To create a fully optimized production installation that utilizes database replication and multiple servers, use the Platform Installation Guide
- To learn more about the latest release, see the ISV Release Notes
- See also these additional resources for installation and configuration:
Installation Requirements
Hardware Requirements
| Application Server |
|
Software Requirements
Installing MySQL Version 8.0.xx
| Operating System |
| ||
| MySQL Server |
If you are a platform user, see Configure the MySQL Server.
| ||
| Libraries | Download the third-party libraries and save them in a folder. You may want to integrate them into the system during the installation.
scrollTolerantForwardOnly=true
|
Installing MySQL Version 5.7.xx
| Operating System |
|
| MySQL Server |
If you are a platform user, see Configure the MySQL Server. |
| Libraries | Download the third-party libraries and save it in a folder. You may want to integrate them into the system during the installation. |
Required for Basic Platform Functionality
| Mail Server |
An email message should be received at the specified address. If the confirmation message does not arrive, check the mail log to discover the cause.
|
| Cache |
Ehcache is available in the Common Tomcat profile. For more information, see Configuring Ehcache. |
| Web Server |
The Apache web server can be placed in front of the Tomcat appserver to deliver static content more efficiently.
For more information, see Installing and Configuring Apache for Use with the Platform. |
| Java |
The installation and operation of the AgileApps Cloud platform requires Java 8. However, the custom code in Java Class continues to be validated against Java 6 syntax as the instrumentation engine responsible for monitoring resource utilization works only on Java 6 byte codes. |
| Browser Support |
As part of the security processes, the Remember me on this computer option is removed from the browser's login page.
|
Required for Additional Functionality
| OpenOffice (optional) |
| ||
| HornetQ (optional) |
The Messaging Server is an optional platform component that:
Get HornetQ from http://www.jboss.org/hornetq/downloads.html. For more information, see Installing the Messaging Server. | ||
| Charting Libraries (optional) |
Additional libraries are needed to email a chart or a report. For more information, see Install the Chart Handling Libraries. |
Installation
Configuring the MySQL Server
These instructions apply to the version of MySQL specified in the Software Requirements.
Terminology:
- MySQL Server
- The database server which has MySQL Server software installed, configured, and running.
- MySQL Client
- Any other computer which connects to the database server and has the MySQL Client software installed, configured, and running.
- The client connects to the database server to access data, for example, webserver.
- Configuration file
- my.cnf, a MySQL configuration file that may be edited and used in the MySQL client or MySQL Server installation.
MySQL Settings
- Storage Engine
- default-storage-engine = innodb
- Server System Variables Configuration
- It is observed that READ_UNCOMMITTED does not work well with Row-Based Replication. Use one of the following configurations:
- a) Either STATEMENT-BASED or MIXED replication with the Transaction Isolation level dictated by business needs.
- b) ROW-BASED replication with transaction_isolation = READ-COMMITTED
- User Configuration
-
- Create a user account with password in MySQL
The Application Server will use the user details.
- The user account should have all MySQL privileges enabled on all databases
- Use the default root account that is created during the installation of MySQL. You can also create a non-root MySQL user to run Agile Apps. For more information, see Creating a non-root MySQL User to Run Agile Apps.
- Create a user account with password in MySQL
- sql-mode Configuration
-
- Add the following code to the my.cnf file located in the MySQL Client:
- sql-mode="PIPES_AS_CONCAT,ANSI_QUOTES"
- Add the following code to the my.cnf file located in the MySQL Server:
- sql-mode="PIPES_AS_CONCAT,ANSI_QUOTES"
- MySQL Configuration for UTF-8 Unicode character set for 5.7 Version
-
- Add the following code to the my.cnf file, located in the MySQL Client:
- default-character-set=utf8
- Add the following code to the my.cnf file, located in MySQL Server:
- character-set-server=utf8
- collation-server=utf8_general_ci
- The character set defines how records can be alphanumerically ordered (or grouped, sorted, filtered, indexed). The list of supported languages is determined by the character set available at the server level. Hence, the UTF-8 Unicode character set configuration is required as part of MySQL configuration.
- To specify character settings at MySQL configuration time:
For MySQL Version 5.7, see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/charset-applications.html
- To specify character settings at MySQL configuration time:
- MySQL Configuration for UTF-8mb4 Unicode character set for MySQL 8.0 Version
Note: For MySQL configuration v5.7 to v8 upgrade, refer Upgrading to MySQL v8.
- Add the following code to the my.cnf file, located in the MySQL Client:
- default-character-set=utf8mb4
- Add the following code to the my.cnf file, located in MySQL Server:
- character-set-server=utf8mb4
- collation-server=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
- The character set defines how records can be alphanumerically ordered (or grouped, sorted, filtered, indexed). The list of supported languages is determined by the character set available at the server level. Hence, the UTF-8 Unicode character set configuration is required as part of MySQL configuration.
- To specify character settings at MySQL configuration time:
For MySQL Version 8.0, see http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman//8.0/en/charset-applications.html
- To specify character settings at MySQL configuration time:
- max_allowed_packet Configuration
- Add max_allowed_packet = 64M to my.cnf or my.ini
- For MySQL Version 5.7, see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/charset-applications.html
- For MySQL Version 8.0, see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/charset-applications.html
- Restart the MySQL server to implement the changes
- regexp_time_limit Configuration
The regular expression limit is expressed as the maximum permitted number of steps performed by the match engine, and thus affects execution time only indirectly. It is defined in milliseconds.
- Add regexp_time_limit=2048 to my.cnf or my.ini
- For MySQL Version 5.7, see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/charset-applications.html
- For MySQL Version 8.0, see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/charset-applications.html
- Restart the MySQL server to implement the changes
Populate the Timezone Tables
- The platform uses MySQL's timezone tables for timezone conversions. These tables are not automatically populated when MySQL is installed, so it necessary to do so after installation.
- Run the following program to initialize the MySQL timezone tables:
- mysql_tzinfo_to_sql /usr/share/zoneinfo | mysql -u root mysql
- where /usr/share/zoneinfo is the standard Linux location for the time zone files. (Your system may differ.)
- For MySQL Version 5.7, see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/mysql-tzinfo-to-sql.html
- For MySQL Version 8.0, see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/mysql-tzinfo-to-sql.html
- mysql_tzinfo_to_sql /usr/share/zoneinfo | mysql -u root mysql
Installing and Upgrading the Application Server
New Installations
- Review the Installable Version Release Notes.
- Ensure that the Hardware Requirements are met.
- Ensure that the Software Requirements#Required for Installation are met.
- Configure the MySQL Server so it is ready for use.
- Ensure that all database servers and web servers are configured to be in the same timezone, regardless of where they are geographically located.
- Use the standard SoftwareAG webMethods installer to install the platform of your choice.
Learn more:- From the webMethods documentation page consult the respective Installation document.
- For the very first server that is installed, Start the Application Server to verify that everything is working.
- For subsequent servers, Configure Backend Services before startup.
- Install the Platform License
- Once installed, proceed to Configuring the Application Server
Upgrades
Important:
These are instructions are for version 10.5 and later.
If you are upgrading to 10.5, use the 10.5 Upgrade Process, instead.
- If you have not already done so:
- Review the Installable Version Release Notes.
- Ensure that the Hardware Requirements are met.
- Ensure that the Software Requirements#Required for Installation are met.
- Backup the platform databases.
- Use the standard SoftwareAG installer to install the 10.5 platform.
Learn more: In webMethods documentation page see the 9.9 Installation document. - Start the Application Server
- When done, proceed to Configuring the Application Server
Configuration
Configuring the Application Server
- As described in Software Requirements#Required for Basic Platform Functionality:
- Configure an email server to enable email-based collaboration.
- To improve performance, install and memcached for caching. (You will configure it in a moment).
- Add the Apache HTTP server to further improve performance.
- All backend services are enabled by default. But they will cause performance problems if they are running on the customer-facing application server, and errors can result if they are running on multiple servers. After installing the platform, therefore, it is important to disable all backend services that are not required on the current server.
- Learn more: Managing Backend Services
- As described in Software Requirements#Required for Additional Functionality:
- To allow PDFs to be generated from documents, install OpenOffice.
- To allow for Collision Detection and Prevention, install HornetQ.
- To be able to email a chart or report, Install the Chart Handling Libraries.
- Additionally:
- Enable One-Click Document Viewing.
- Add Multibyte Character Fonts for PDF printing.
- To enable Java Code Governors on Red Hat 6, perform the steps mentioned in the Additional Step for RedHat article.
Note:
When making changes to an existing server, restart the server to read in the new values.
Configure the Service Provider Settings
Accessing the Application Server
After the application server has been started:
- 1. Access the Service Provider URL: http://{yourDomain}/networking/Service?t=1&targetpage=ViewPort.jsp:
- Where:
- {yourDomain} is the platform domain. For example: yourcompany.com
- Default username and password: Use the credentials you typed into the Software AG installer.
- The platform will request that you change your password after you login the first time.
- 2. Setup the Service Configuration with these required parameters:
- Configure the Service Settings and specify Service and Domain names:
Parameter Description Typical Value Service Name Name of the service provider Financiocorp Services Prefix for Service Domain Optional subdomain name Allowed characters: a-z, A-Z, 0-9, - (alphanumeric, plus hyphen)
Example: service
Service Domain The Domain Name part of the URL mydomain.com Domain URL Read Only
Automatically populated as:- Prefix + Service Domain
service.mydomain.com
Set Up the Initial Tenant
At this point, you are working with the tenant administration interface. The next step is to create a tenant. Logging into that tenant brings up the application interface, where you can build, load, and run applications. (It also makes recovery easier, should you make a mistake. For example, were to you "delete all", you could always create a new tenant, since the underlying platform would be unaffected.)
Creating a Tenant
- After Login, create a new tenant from a web browser using the URL as follows:
- https://yourdomain.com/networking/Service?t=2308
- Where yourdomain.com is the name of your domain
You are now ready to begin application development or install an existing application for testing.
See the Welcome page for links to additional information on those subjects.
Application Server Operations
Server Restart Sequence
When an installation employs memcached or the Messaging Server, it is important to follow this sequence when restarting servers:
- <syntaxhighlight lang="bash" enclose="div">
- STOP THE MESSAGING SERVER, if one is running:
/etc/init.d/messaging stop {hornetq-folder}/bin/stop.sh
- STOP ALL APPLICATION SERVERS
- On each server:
{install-dir}/profiles/IS_default/bin/shutdown.sh
- STOP ALL memcached SERVERS
- On each server:
/bin/memcached -d stop
- START ALL memcached SERVERS
- On each server:
/bin/memcached -d start -p {port} -u {user} -m {MB_of_memory}
# Typical values: # Port: 11211, User: root, MB of memory: 25
- START ALL APPLICATION SERVERS
- On each server:
{install-dir}/profiles/IS_default/bin/startup.sh
- START THE MESSAGING SERVER, if you're running one:
{hornetq-folder}/bin/start.sh /etc/init.d/messaging start </syntaxhighlight>
- Considerations
-
- Stopping application servers ensures that they aren't adding entries to the cache.
- Stopping memcached makes sure that the cache is flushed.
- Those two steps can occur in either order. It is the next two for which order is critical:
- Restarting memcached first makes sure that a clean copy of the cache is available.
- When the application servers come up, they use the clean cache.
Start the Application Server
- Login as root
- {install-dir}/profiles/IS_default/bin/startup.sh
Restart the Application Server
- Login as root
- {install-dir}/profiles/IS_default/bin/restart.sh
Stop the Application Server
To stop the application server, you kill the Apache Tomcat container it's running in.
- Login in as root
- {install-dir}/profiles/IS_default/bin/shutdown.sh
Accessing the Application Server
After the application server has been started:
- 1. Access the Service Provider URL: http://{yourDomain}/networking/Service?t=1&targetpage=ViewPort.jsp:
- Where:
- {yourDomain} is the platform domain. For example: yourcompany.com
- Default username and password: Use the credentials you typed into the Software AG installer.
- The platform will request that you change your password after you login the first time.
- 2. Setup the Service Configuration with these required parameters:
- Configure the Service Settings and specify Service and Domain names:
Parameter Description Typical Value Service Name Name of the service provider Financiocorp Services Prefix for Service Domain Optional subdomain name Allowed characters: a-z, A-Z, 0-9, - (alphanumeric, plus hyphen)
Example: service
Service Domain The Domain Name part of the URL mydomain.com Domain URL Read Only
Automatically populated as:- Prefix + Service Domain
service.mydomain.com
Creating a Tenant
- After Login, create a new tenant from a web browser using the URL as follows:
- https://yourdomain.com/networking/Service?t=2308
- Where yourdomain.com is the name of your domain